Welcome to On Verticality. This blog explores the innate human need to escape the surface of the earth, and our struggles to do so throughout history. If you’re new here, a good place to start is the Theory of Verticality section or the Introduction to Verticality. If you want to receive updates on what’s new with the blog, you can use the Subscribe page to sign up. Thanks for visiting!
Click to filter posts by the three main subjects for the blog : Architecture, Flight and Mountains.

Introduction to Verticality
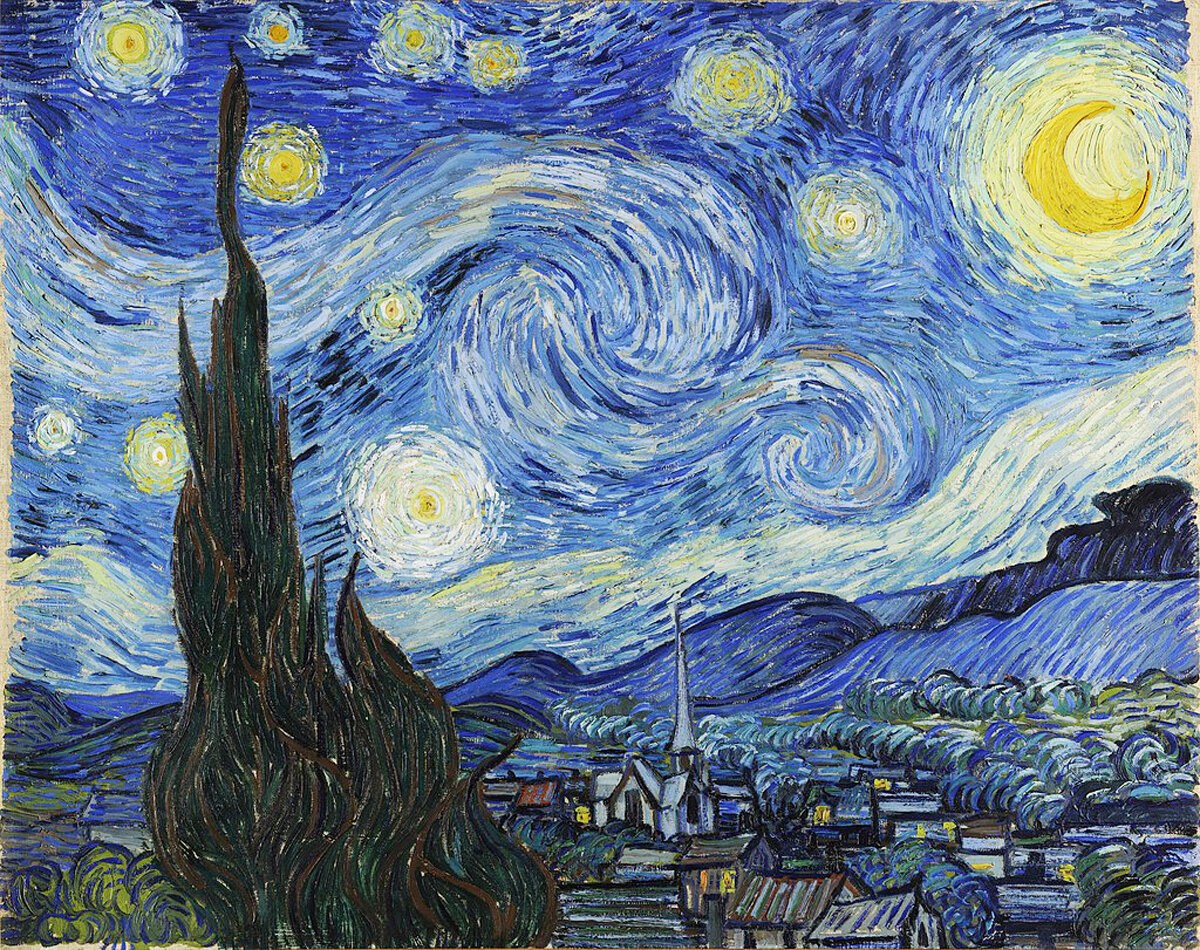
Ever since humans descended from the trees and out onto the savannah, we’ve gazed upward in wonder at the sky and the stars. Until fairly recently in our history, this space above our heads was a mystery. Our ancestors would witness the diurnal movements of the Sun and the Moon, and the brilliance of a glowing sunrise or sunset. The clouds would drop water and thundering bolts of light and energy. At night, they would witness a spectacular tapestry of light-emitting dots, and connect them into elaborate shapes. The sky has been a continual source of wonder throughout our history, and we’ve spent countless hours thinking about the world we see above our heads.

Verticality, Part XII: A Never-ending Struggle
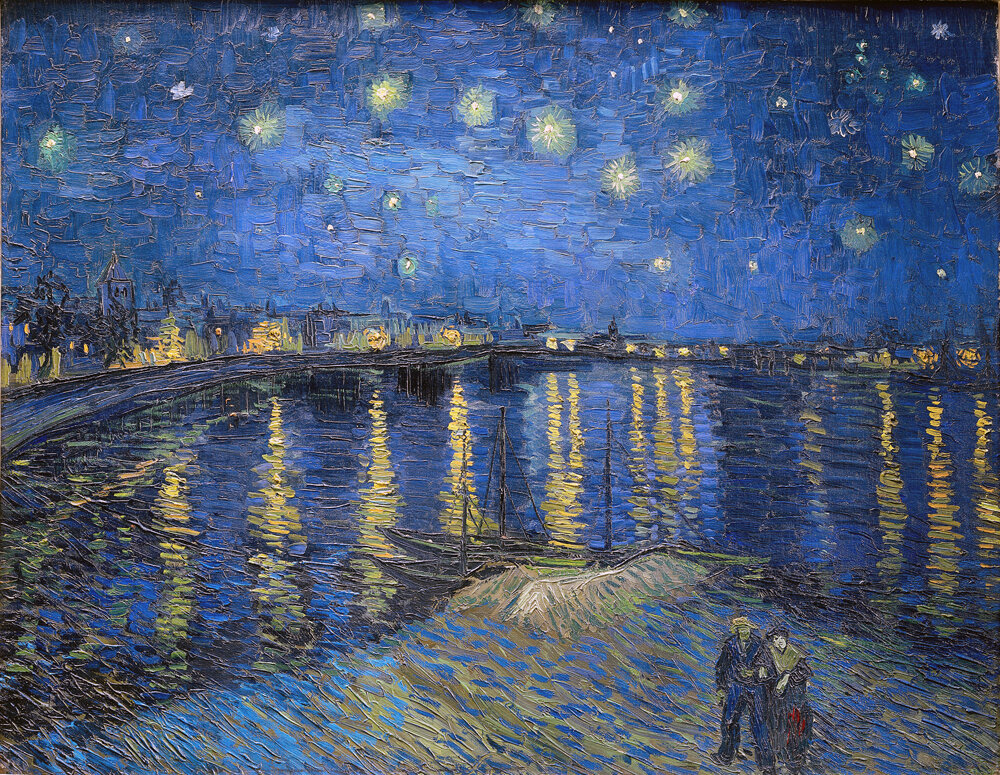
The preceding work has explored our history with Verticality and our struggles to escape the surface of the Earth throughout human history. It began with our context on Earth and our source code that developed in us before we became human in the first place. It then explored our subsequent history up to today and focused on architecture, which is an external manifestation of this inner need to escape the surface. The previous chapter brought us to the present day, which also brings us to the question: will we ever stop pursuing our need for Verticality?
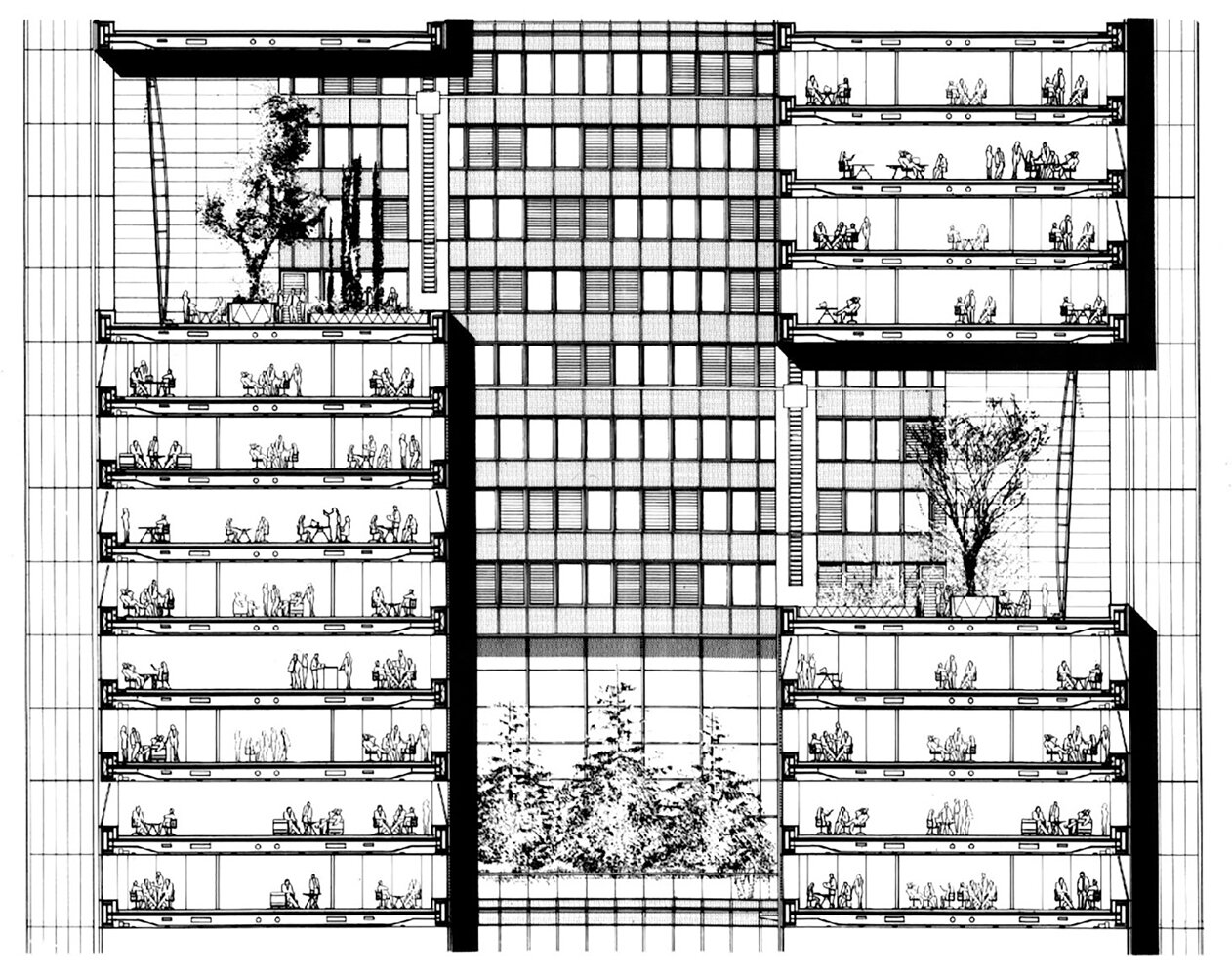
Verticality, Part XI: Breaking the Box
A rebellion against spacecraft and efforts to humanize the tall building
The human experience of stacked, identical floors on top of one another was foreign to our surface-dwelling nature. The disconnected, isolated experience of International Style buildings took us up to the sky, but cut us off from everything surrounding us. This lack of variety in tower floors and the monotony of box-like tower forms would begin to be challenged by architects. This signaled that we needed to humanize our experience of Verticality again. Instead of monotonous boxes, towers began to see their forms eroded away in order to create more varied experiences within them. We needed to recreate the surface in the sky.

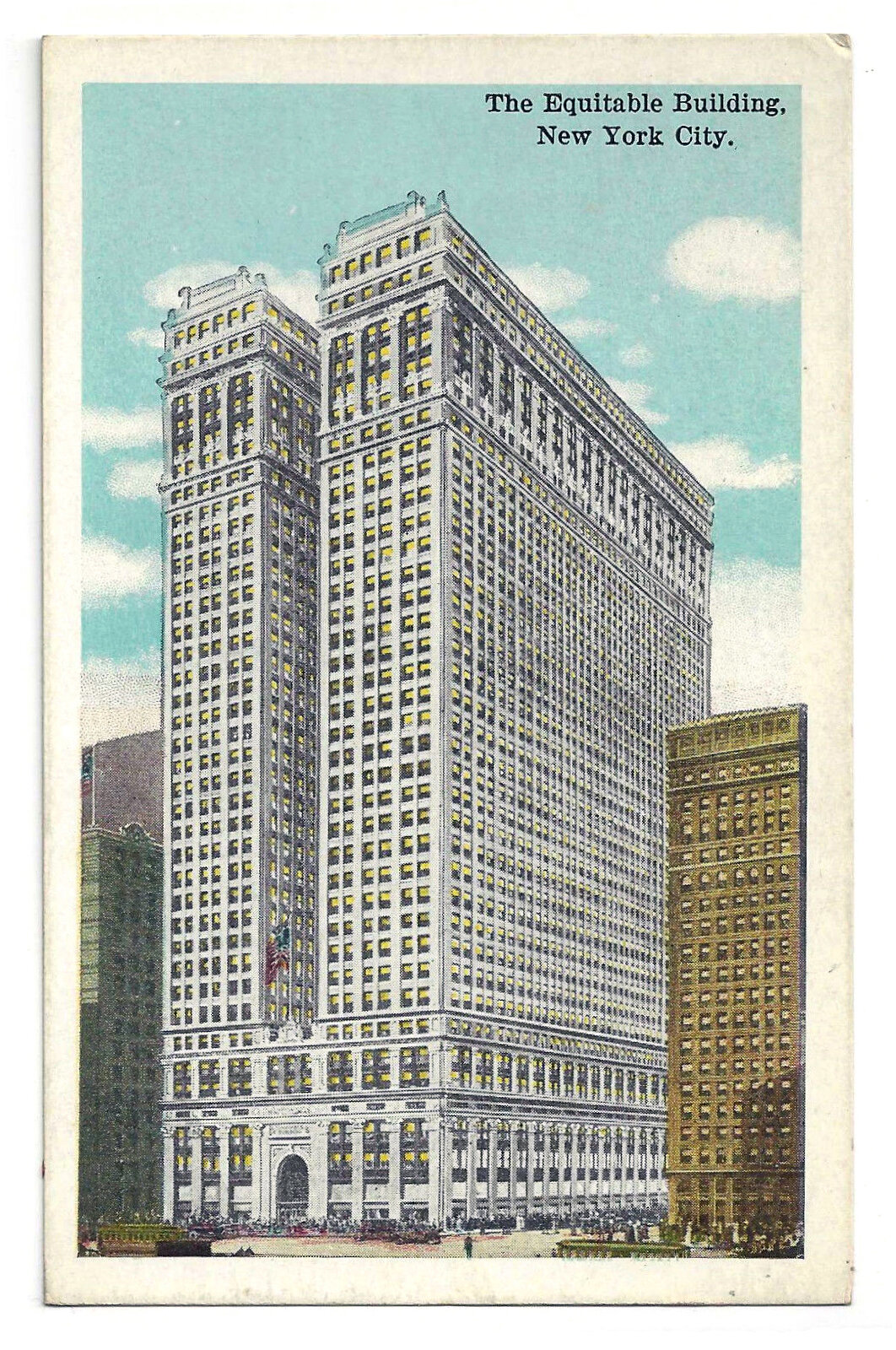
Verticality, Part X: Conquering The Skies
The construction of the Equitable Building in 1915 ushered in a new age of skyscraper design. Humans were now able to escape the surface of the Earth with our interior environments, and our need for Verticality had ceased to be driven by the unknown. It was now driven by our need to congregate through density and to distinguish ourselves from one-another. Ego had replaced God, and as a result our quest for Verticality would become synonymous with human achievement.

Verticality, Part IX: Man Upends God
The needs of man become more important than the needs of God
After the Renaissance, humanity would largely abandon our ambitions to recreate heaven on earth, and our focus would shift to raising up our bodies as far from the surface as possible. Rather than singular, largely empty spaces, our tallest and most ambitious constructions would become containers of stacked spaces, still with Verticality as the ultimate goal. We were beginning to escape the surface.
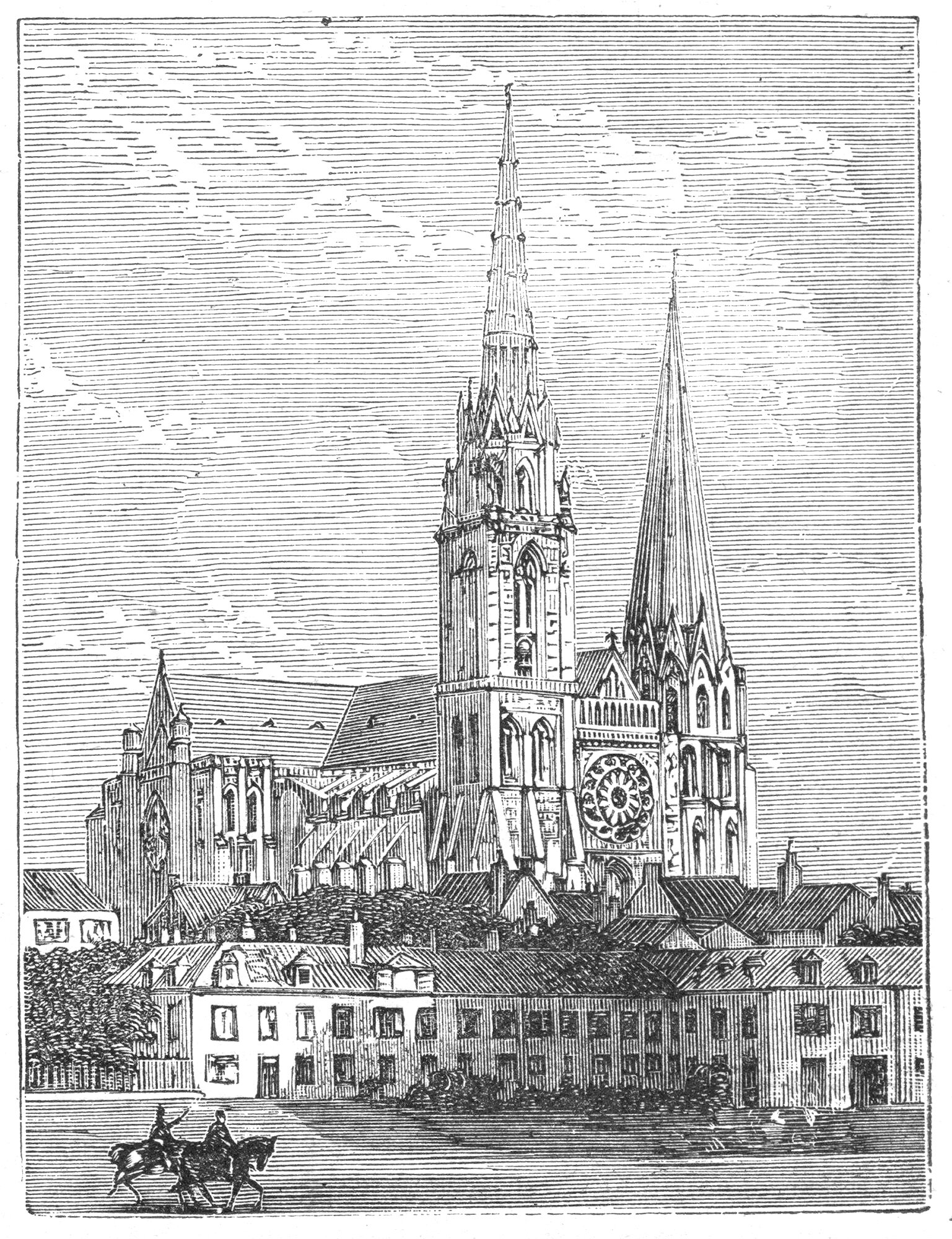
Verticality, Part VIII: God versus Ego
The human world becomes as important as the world of God
The rise of Christianity in the Western world would have profound effects on the built environment and human culture. Two major threads would combine to influence Early Christian architecture and culture. The first is the architecture of the Ancient Romans, who were already wrestling with Verticality. The second is the Book of Genesis and its central theme of Heaven (the above) and Hell (the below). Combine these two, and you get an ongoing battle between God and Ego that would see some of the most impressive structures of all time get built.
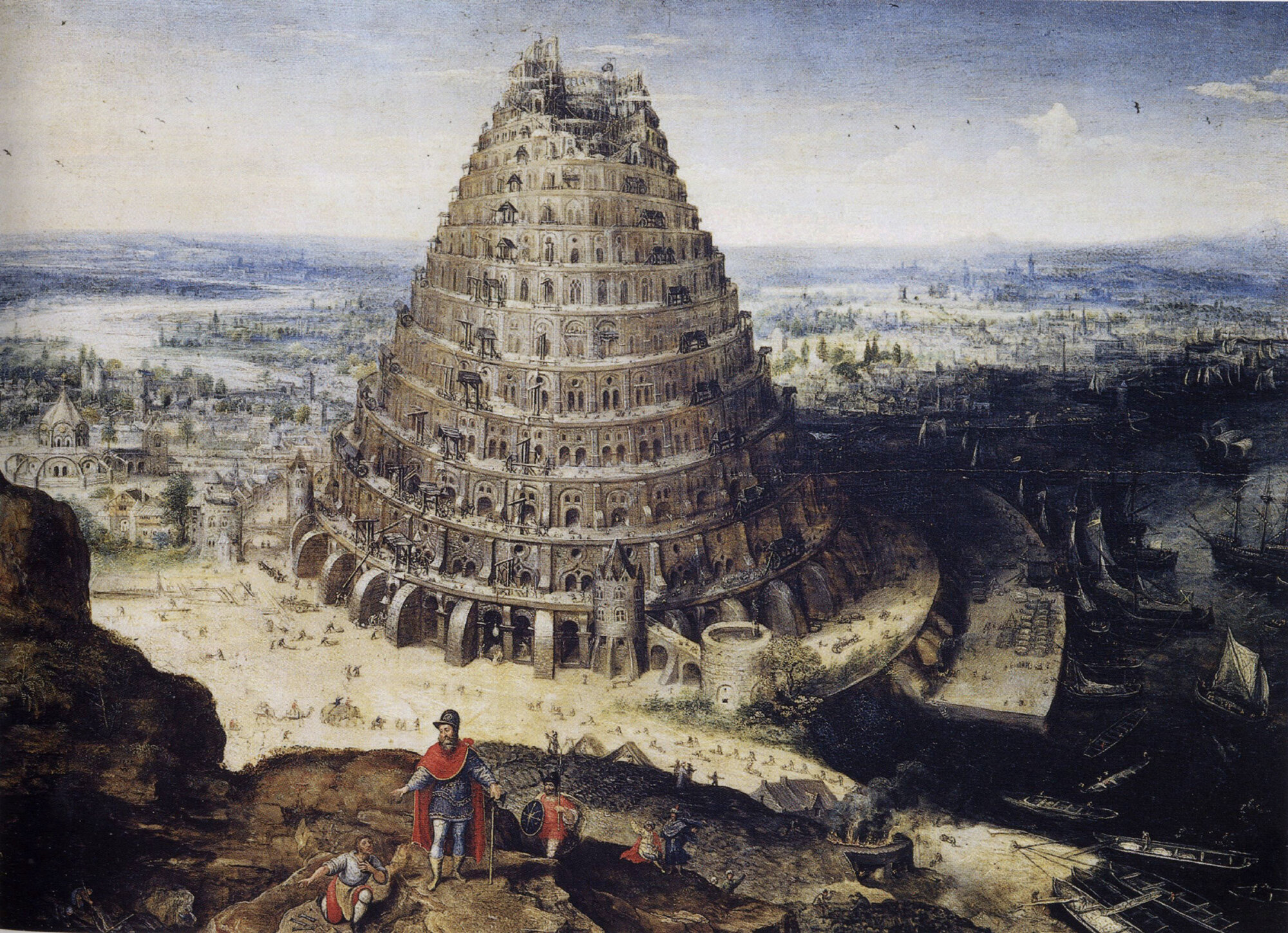

Verticality, Part VII: Heavens on Earth
Humanity’s first major attempts to recreate heaven on earth
In the previous section, we explored ancient civilizations and how they utilized Verticality in their architecture. In each of these civilizations, building a structure that connected the surface to the sky was seen as the pinnacle of human achievement. This was done to appease or satisfy some type of god or gods, and untold amounts of time and effort were spent on the road to achieving it. Throughout time, however, the needs of our gods would begin to see competition from the needs of humanity, or our own Ego.
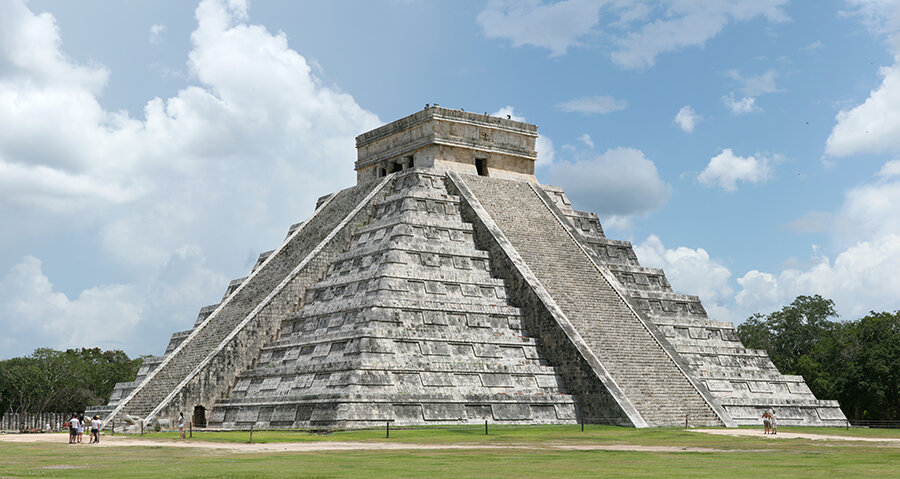

Verticality, Part VI: Archetypes
Man’s initial attempts to get closer to the sky in each of the five cradles of civilization
How does one achieve physical Verticality? At the most basic level, we can get closer to the sky in two ways. First, we can recreate the human body with singular elements that express height on their own. These objects can be seen as proxies for our own bipedal bodies. Second, we can physically raise the surface under our feet in order to raise our bodies up closer to the sky. These constructions can be seen as recreations of mountains, which are the highest places we can reach in the natural landscape. As our ancestors set out to externalize their need for Verticality, they experimented with both of these methods.

Verticality, Part V: Global Threads
How Defense and God provided the initial thrust for the Verticality narrative
Once our ancestors ceased to be nomadic and began establishing permanent settlements, two major threads of our development emerged. The first was the need to defend our territories against others; once we’d accomplished this, our attention shifted to our relationship with the unknown, or God. Each of these threads would evolve over time, and each was approached through the lens of Verticality.

Verticality, Part IV: Beating the System
Homo Sapiens becomes the first animal to escape the food chain
Monkeys and apes are vulnerable creatures. Our source-code was built for a life in the trees, and on our own we lack any natural means of defending ourselves. Compared to other animals that evolved to survive on the savannah, we have no claws or fangs, we’re not particularly quick, and we don’t have natural camouflage. This makes us dangerously vulnerable to predators, and meant we needed to find another evolutionary niche in order to survive. Our answer was power in numbers.
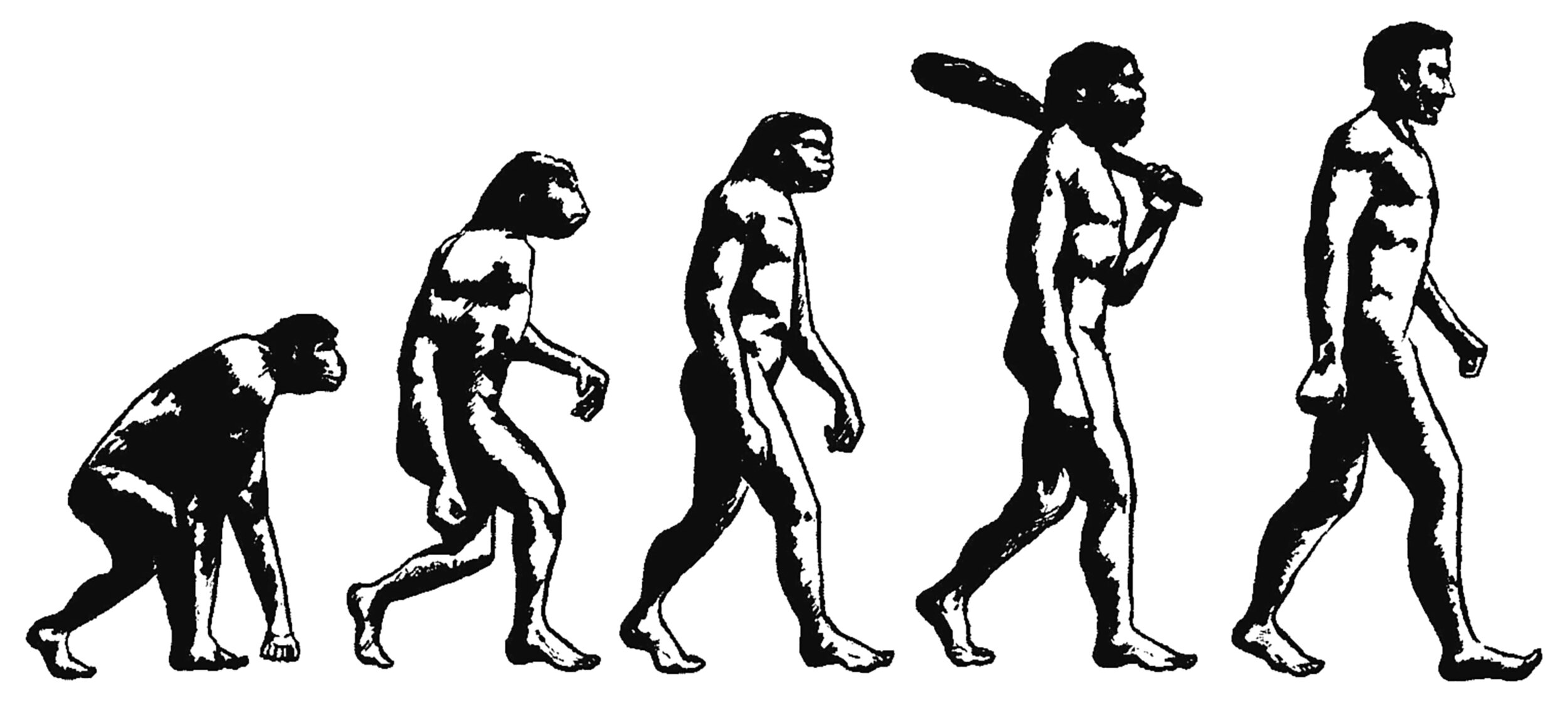
Verticality, Part III: Inception
Our first act of descension and our first act of ascension
Our species evolved within the context described in Part I, and our physical surroundings would provide the foundation for our struggles with Verticality, as described in Part II. These early struggles would be defined by two acts. The first is an act of descension: we came down from the trees and out onto the savannah to become surface-dwellers. We would still carry much of the baggage from tree-dwelling life with us, however. I’ll henceforth refer to this baggage as our source-code. The second is the shift to bipedalism, resulting in our upright, vertical bodies. Together, these two acts would set the stage for the future and our never ending struggle to escape the earth’s surface.
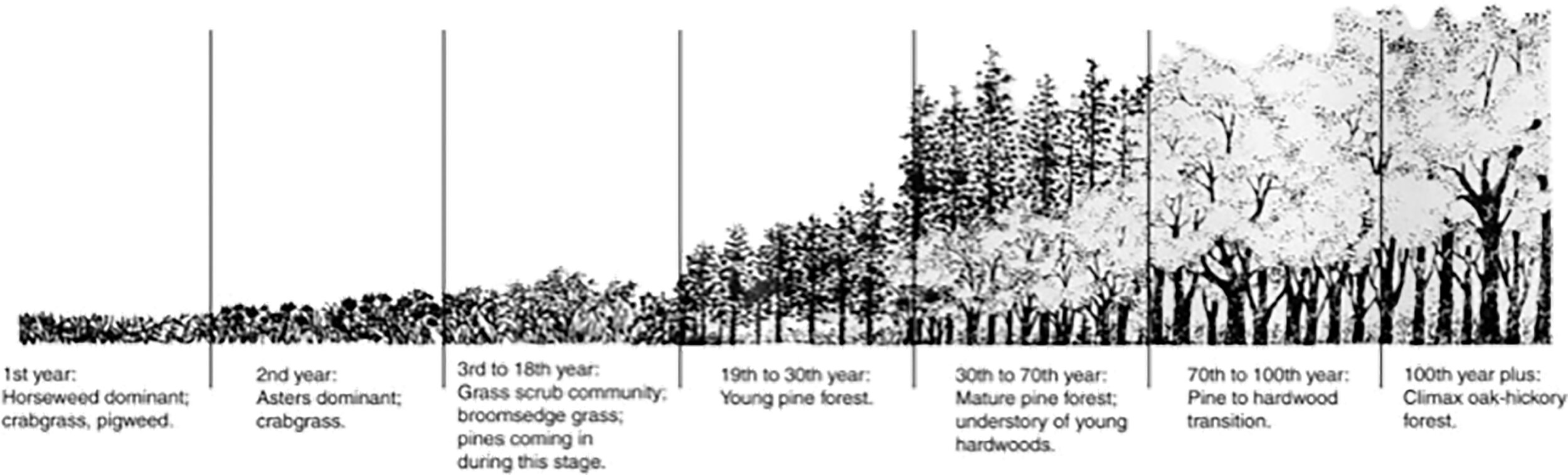
Verticality, Part II: The Seeds of Verticality
Natural phenomena throughout our context that exhibit verticality
So there we were. Confined to the earth's surface, competing with life around us and existing at the center of our own worlds. As our ancestors evolved in the trees, we didn’t have the means to shape our environment like we do today, so we had to look to the natural landscape of the earth’s surface to satisfy our need for Verticality and exploit them whenever possible. These natural phenomena would define our early relationship and struggles with the surface, the sky, and the underground.
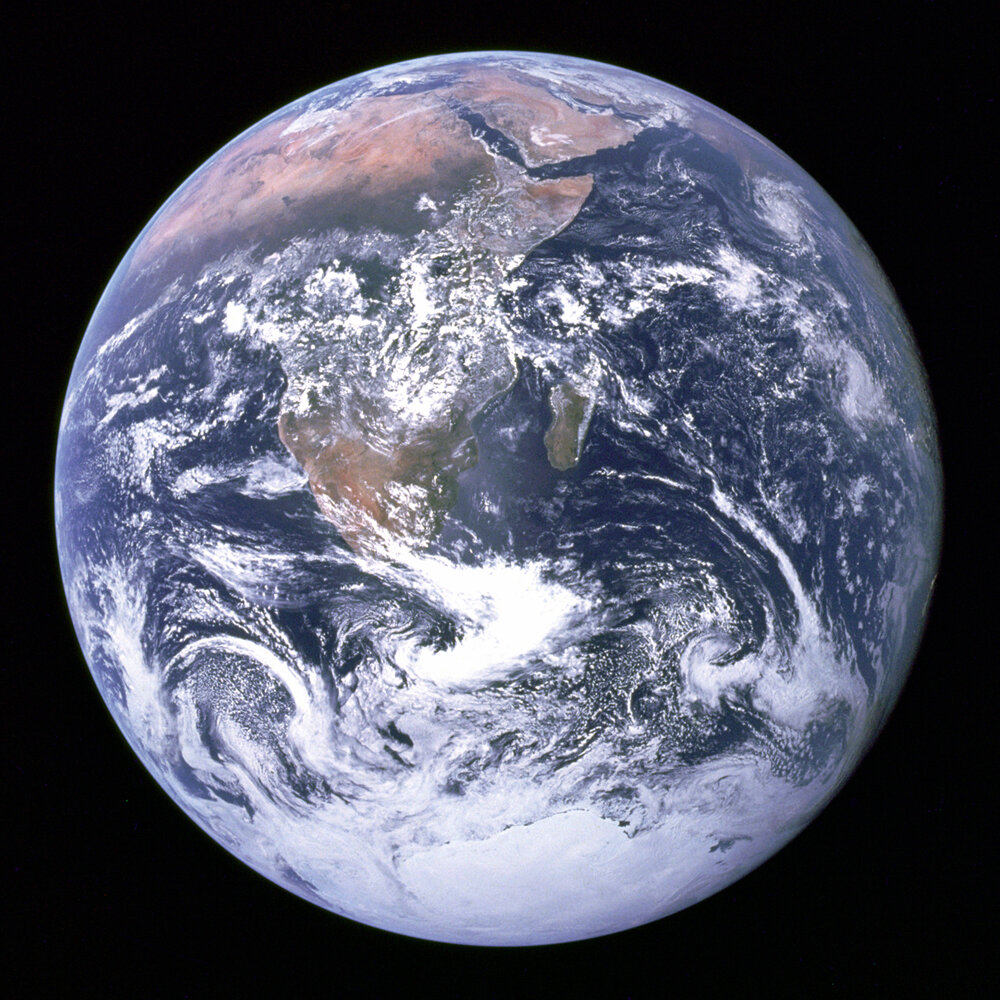

Verticality, Part I: The Context
The universal elements of our lives on planet earth
In order to understand how and why humans have an innate need to escape the surface of the earth, we must first examine the context in which we have evolved and existed throughout our history. This context is unchanging, and has been true for every member of our species who has ever lived. I’ll approach the subject in two parts.
