Welcome to On Verticality. This blog explores the innate human need to escape the surface of the earth, and our struggles to do so throughout history. If you’re new here, a good place to start is the Theory of Verticality section or the Introduction to Verticality. If you want to receive updates on what’s new with the blog, you can use the Subscribe page to sign up. Thanks for visiting!
Click to filter posts by the three main subjects for the blog : Architecture, Flight and Mountains.
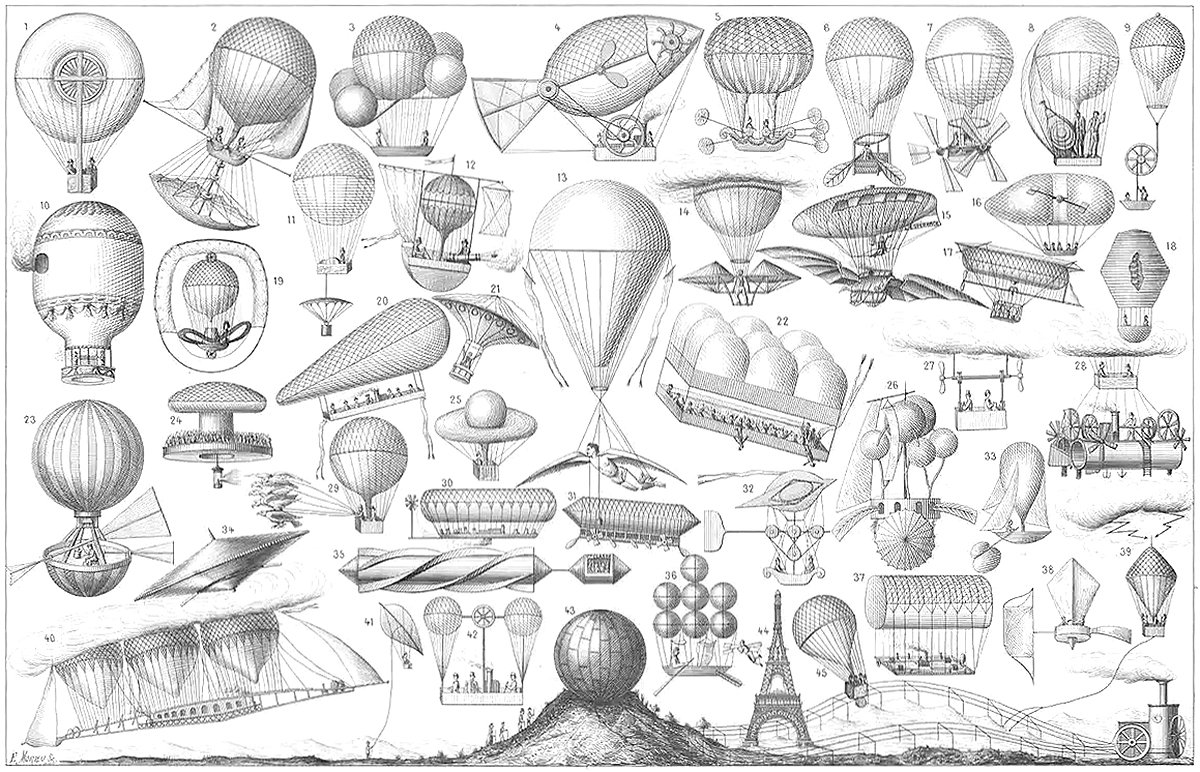
A Compendium of Dirigibles
Pictured above is an exhaustive collage of early dirigible designs, circa 1885 by E. Morieu. As far as I can tell, there’s forty-five designs in total, and many of them seem quite unique. Most likely the original print was paired with a descriptive list, but unfortunately this link has since been broken. Even so, there’s great beauty in the variety of the designs shown here, as well as the creative spirit that led to all of them. A collage like this is evidence of the human need for verticality, that all these individuals would put so much time and effort into achieving human flight.
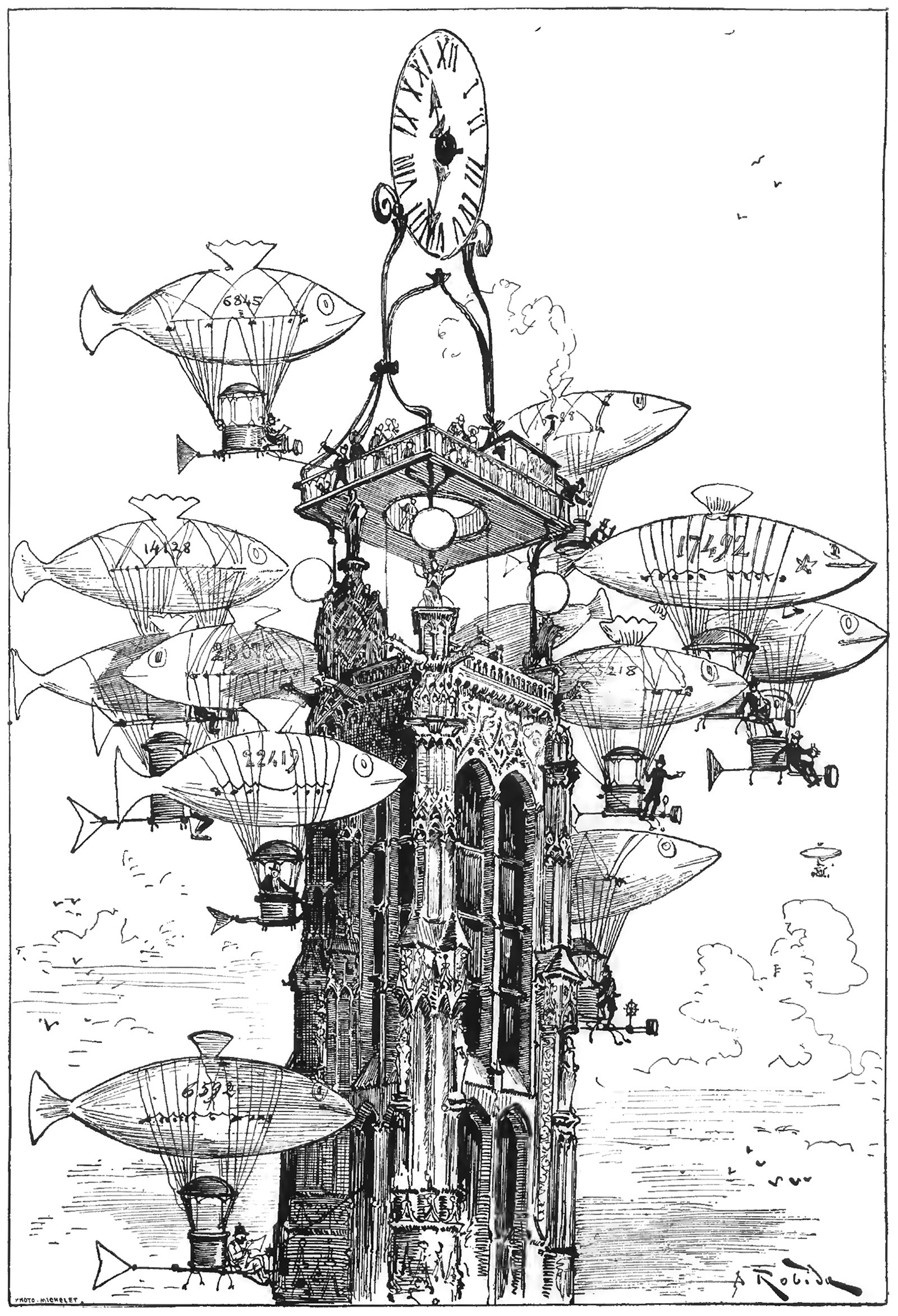
An Aerocab Station atop the Tour Saint-Jacques
The above illustration was drawn by Albert Robida for his 1883 novel Le Vingtième Siècle, or The Twentieth Century. This illustration was titled La Station d'Aerocabs de la Tour Saint-Jacques, or The Aerocab Station of the Tour Saint-Jacques, and it shows a raised platform and clock atop the iconic Parisian structure. Flocking around the tower is a group of dirigibles made to look like fish. What’s charming about the image is how the cluster of dirigibles resemble a school of fish, almost crowding out the tower itself from the image.
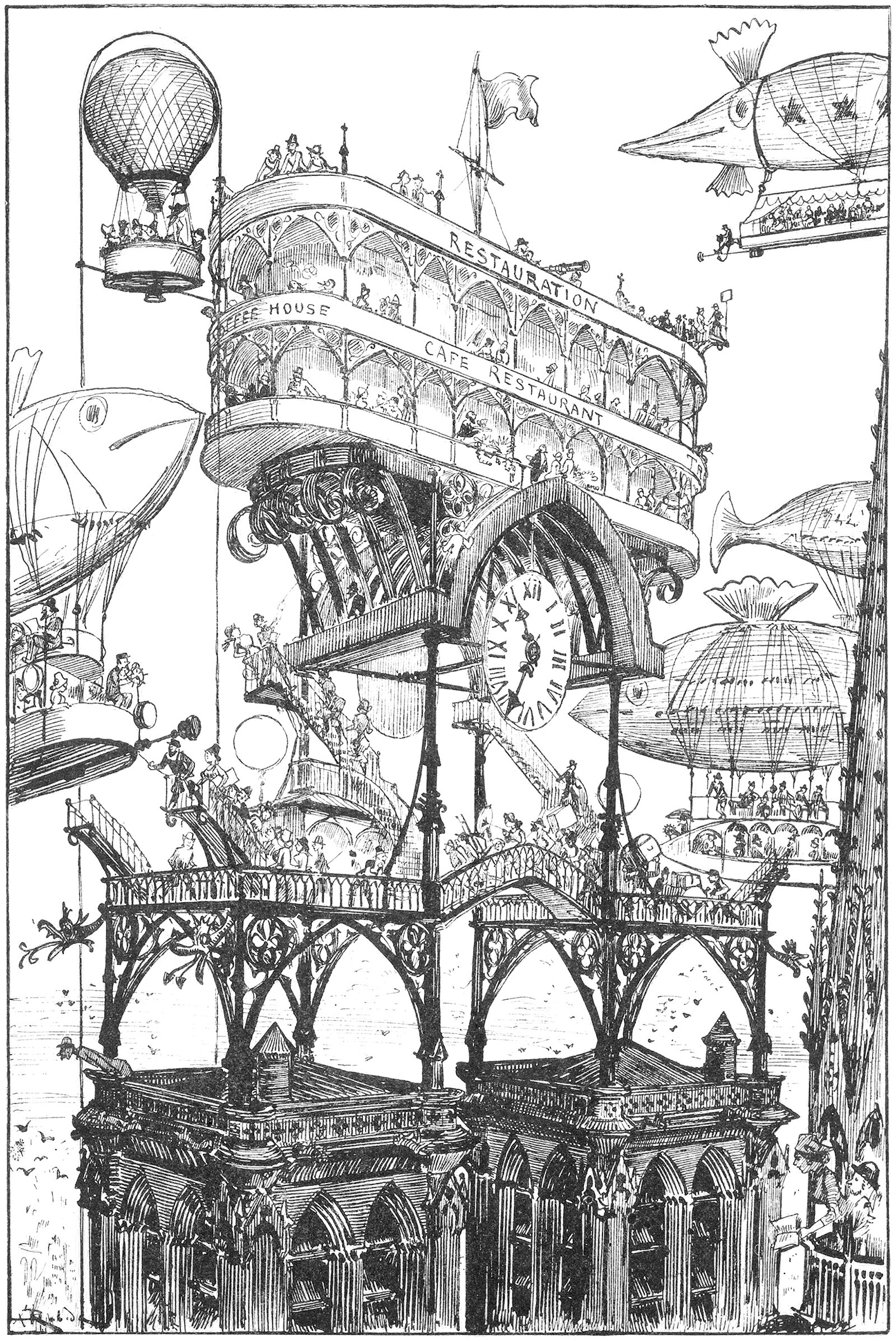
An Airport on top of Notre Dame
The above illustration was drawn by Albert Robida for his 1883 novel Le Vingtième Siècle, or The Twentieth Century. The novel describes a future vision for Paris in the 1950’s, focusing on technological advancements and how they would affect the daily lives of Parisians. Here he shows an elaborate transit station built on top of the bell towers of the Notre Dame Cathedral. It’s a wonderfully ambitious idea, and it represents modernity overtaking history.
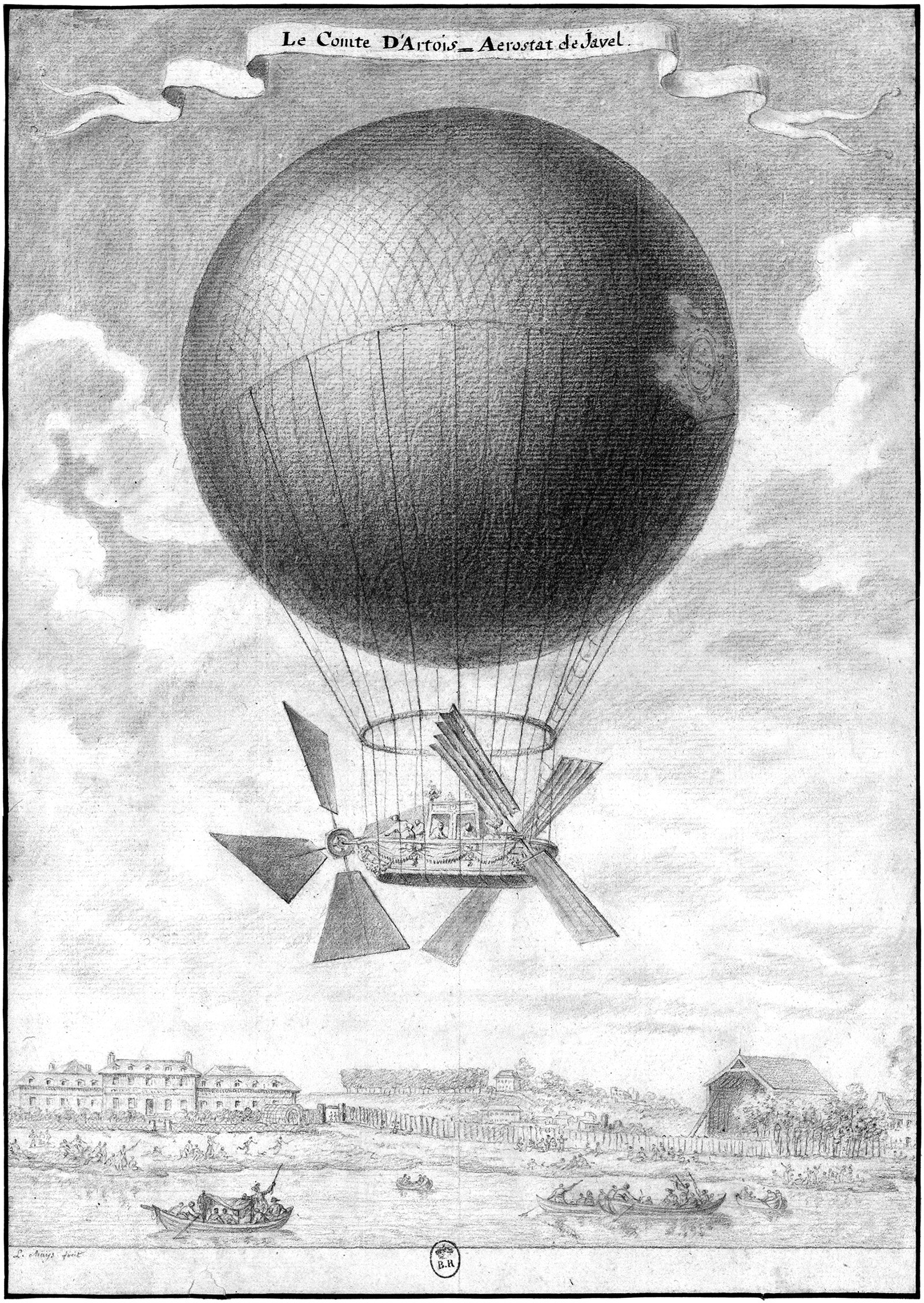
Alban & Vallet’s Comte d’Artois
Pictured above is a design for a flying machine by Léonard Alban and Mathieu Vallet from 1785. It was called Comte d-Artois, or l'Aérostat de Javel. It had a helium-filled balloon which carried a gondola. At one end of the gondola was a large propeller and at the other end was a pair of paddles. The gondola could comfortably seat four people and resembled a shallow boat. Throughout 1785, Alban and Vallet made many successful flights around Paris with the craft, and they also made three notable advancements in ballooning technology along the way.
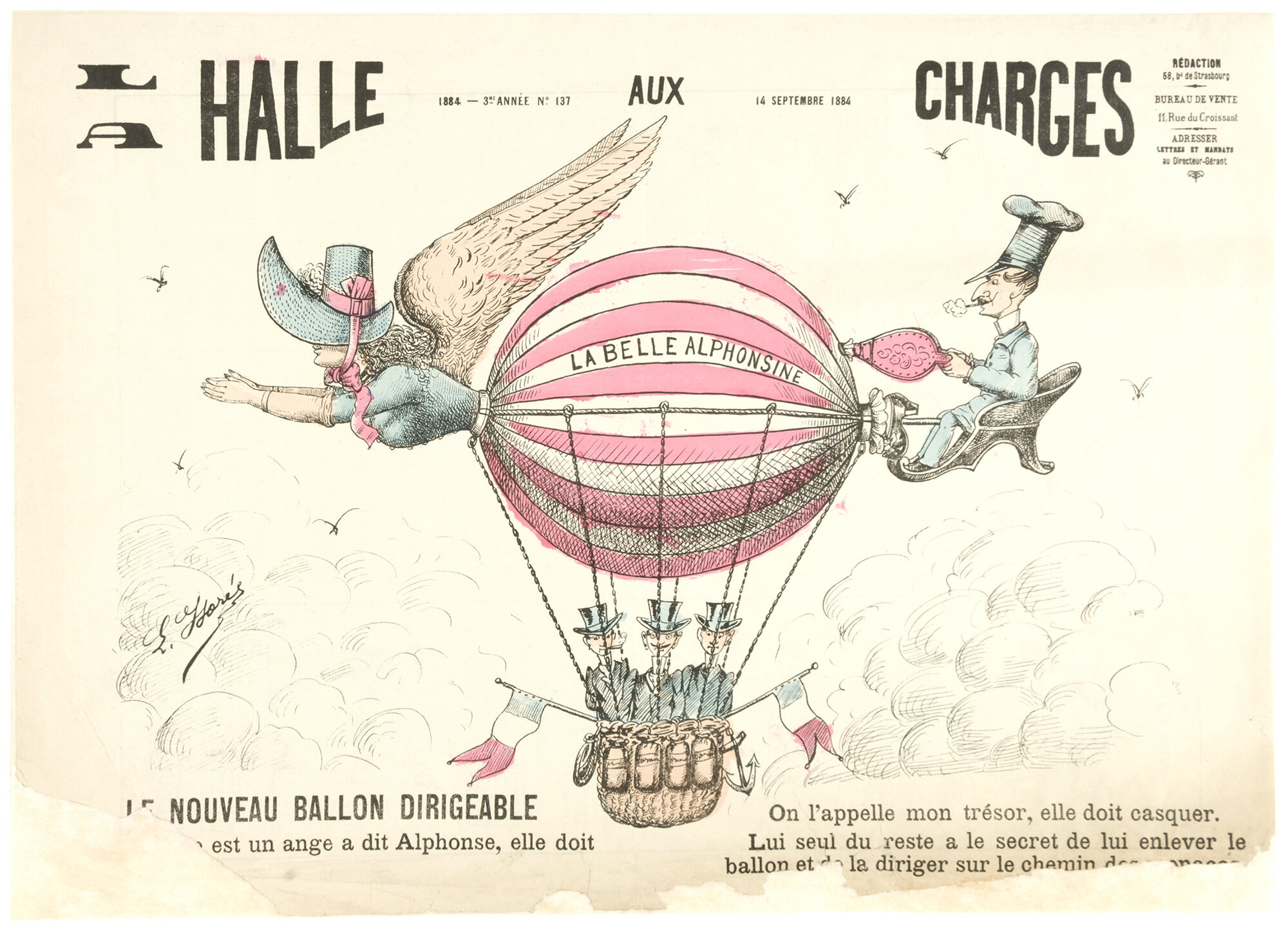
La Belle Alphonsine by E. Florés
In the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries, the human quest for flight was continuously on the public’s mind, and the above illustration is a testament to this. It’s from the front page of a French newspaper called La Halle aux Charges from 14 September 1884. This newspaper was well-known for it’s political caricatures and social commentary, and their choice to put a fictional balloon on their front cover is the perfect representation of what a successful flight means for all those involved.
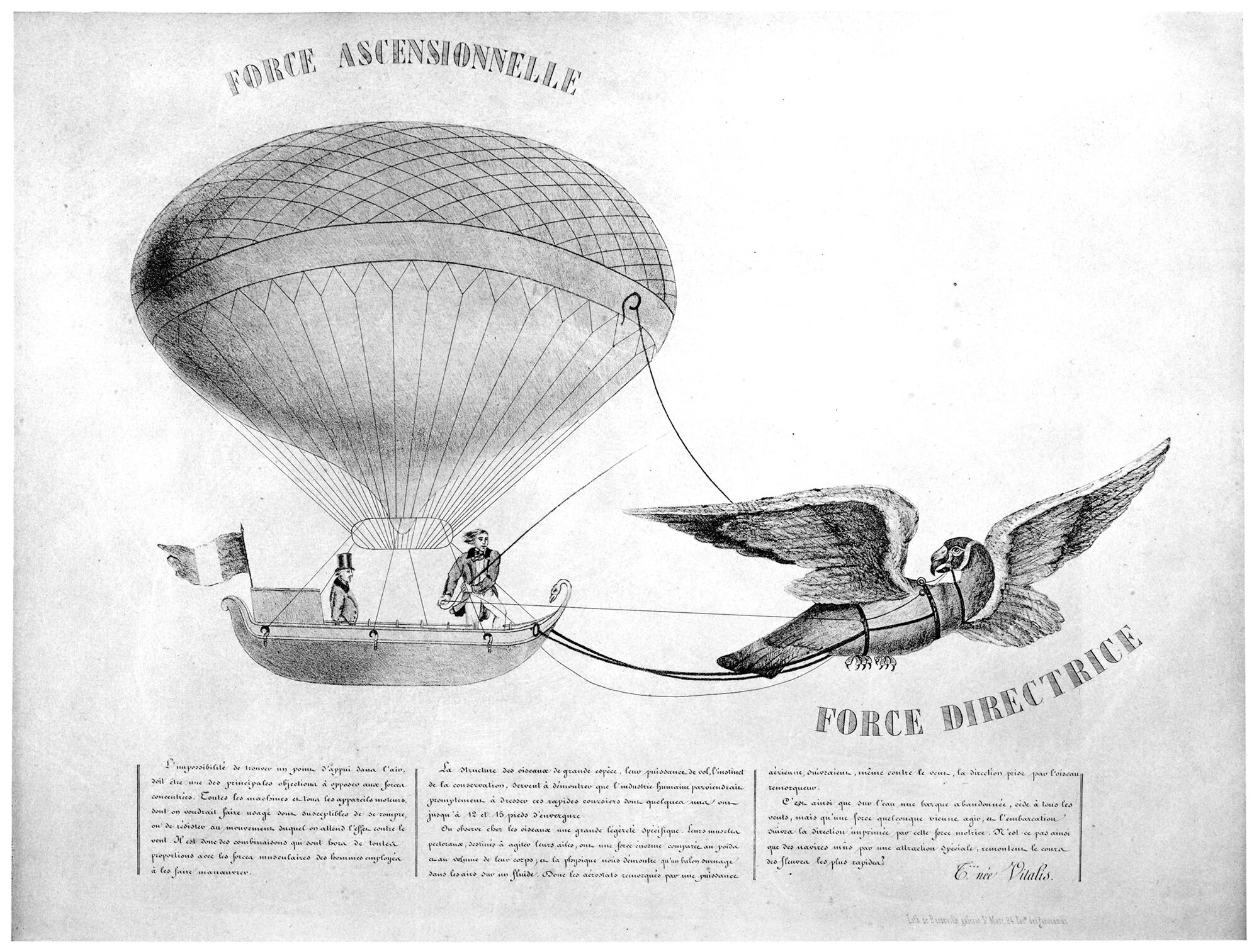
Tessiore’s Balloon Project Towed by a Tame Vulture
Pictured above is a design for a flying machine, consisting of a balloon pulled by a tame vulture. It was originally published in 1845, and was re-published in 1922 in the book L’Aeronautique des origines a 1922. The title of the illustration is Projet de Ballon Remorqué par un Gypaète Spprivoisé, or Project for a Balloon Towed by a Tame Vulture. I’m unable to find any data on the image apart from this, but the content itself is enough to discuss, for obvious reasons.

The Isolation of Flight
Have a look at the above illustration. It shows an airship high up in the clouds, isolated and alone up in the sky. This view encapsulates the idea that humans are surface-dwellers, and we’re not built for a life in the clouds. Throughout our history, we’ve spent untold amounts of time and energy trying to escape the surface of the earth, but the reality of such an escape is so foreign to our needs, that it creates a conflict within us.

Pierre Ferrand’s Corkscrew Airship
This is Pierre Ferrand de Montfermeil’s 1835 design for an airship, featuring a giant screw mechanism and an elaborate system of fins. Unfortunately details of the design are scarce, and this appears to be the only image we have. According to the authors of the book L’Aéronautique des origines à 1922, it originallt appeared in a brochure titled Projet pour le Direction de l'Aérostat par les Oppositions Utilisées, or Project for the Direction of Airships used by Oppositions.
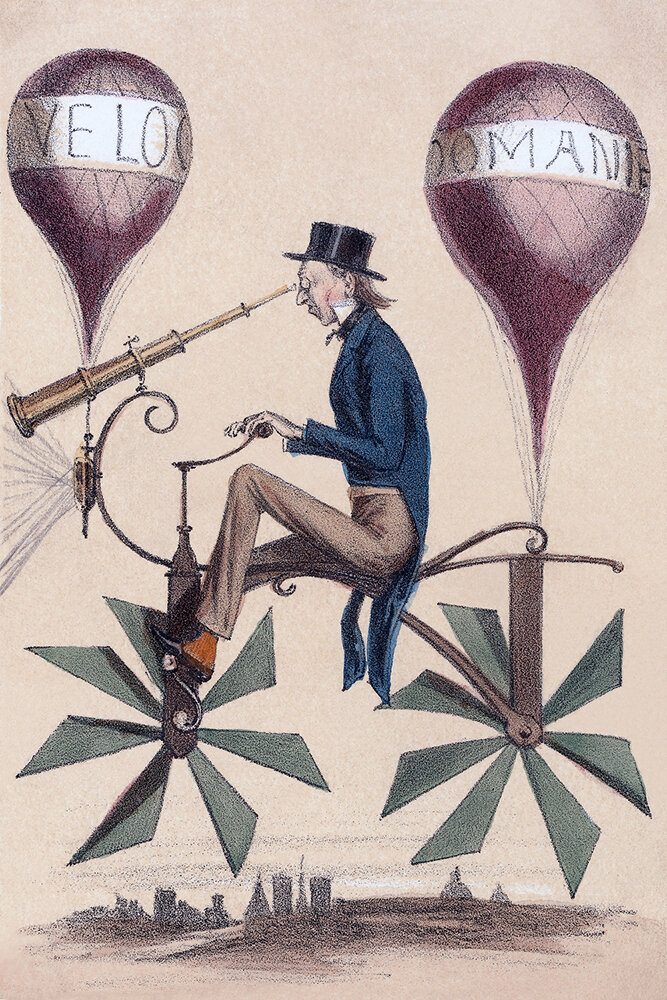
A Voyage to the Moon
There’s a fine line between fiction and invention. Throughout my research into flying machines, I’ve come across many fictional designs that weren’t meant to actually fly, but to evoke the idea of flight. The above cartoon is one of these. It’s a French cartoon from 1867, titled Voyage a la Lune, or Voyage to the Moon. It riffs on the idea of a bicycle that flies, and it’s got a playful feeling about it, as if it doesn’t take itself seriously.
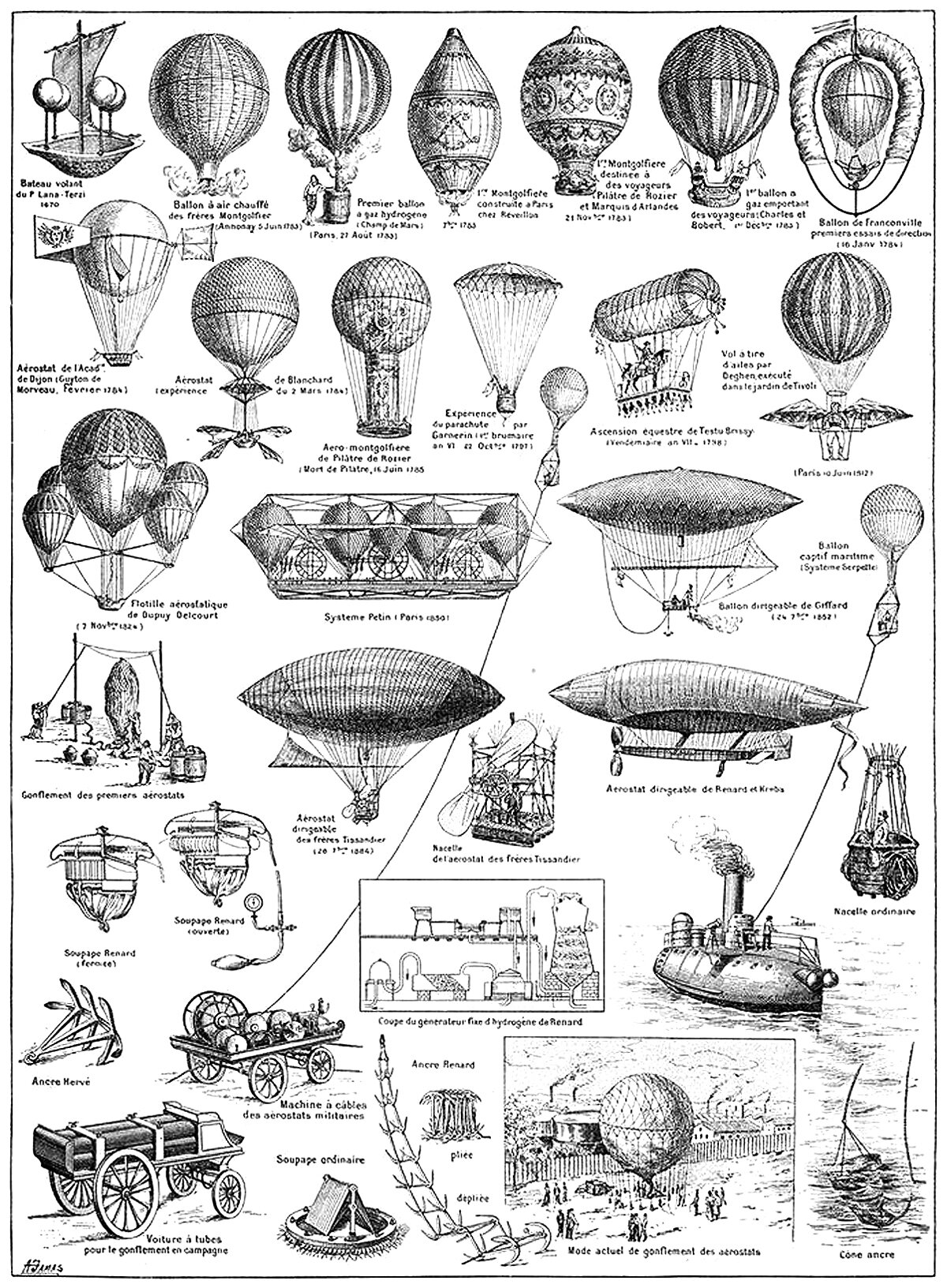
Early Balloon Designs
There are two main strategies when designing a flying machine. The first is a heavier-than-air machine, which relies on creating a lifting force to overcome gravity. The second is a lighter-than-air machine, which relies on a balloon filled with gas or heated air. The above illustration shows famous examples of the latter.
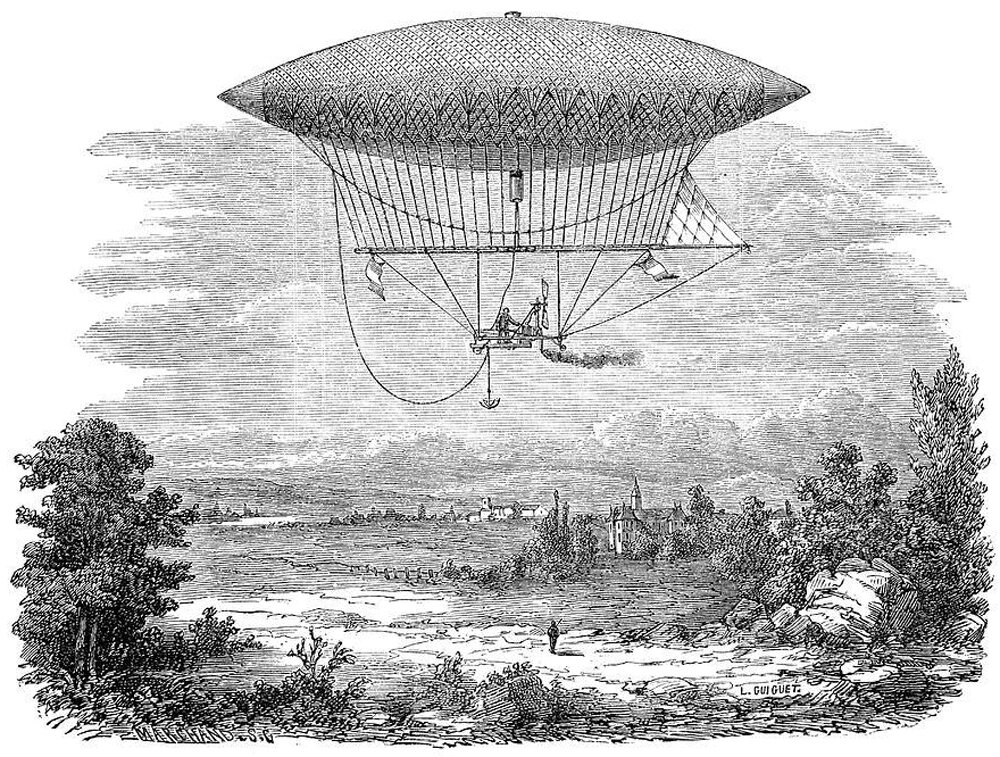
Henri J. Giffard's Airship and Captive Balloon
The airship pictured above was invented by Henri Giffard, which first flew in 1852 from Paris to Élancourt, a journey of 27 km (16.7 miles). I love this image because of the single, solitary figure in the foreground, staring up at the massive airship floating in the sky above. There’s something inspiring about the scale of the two human figures shown, one on the ground looking up, and the other controlling the airship as it floats by, looking down on the landscape below. I see Henri Giffard’s work as an attempt to bring these two worlds closer together.

Francesco Lana de Terzi's Aerial Ship
Francesco Lana de Terzi is sometimes referred to as the Father of Aeronautics. He was an Italian Jesuit priest, a professor of physics and mathematics, and he was intrigued with human flight. In 1670 he published Prodromo, a book containing myriad ideas and inventions, the most famous of which was the design for a flying ship.
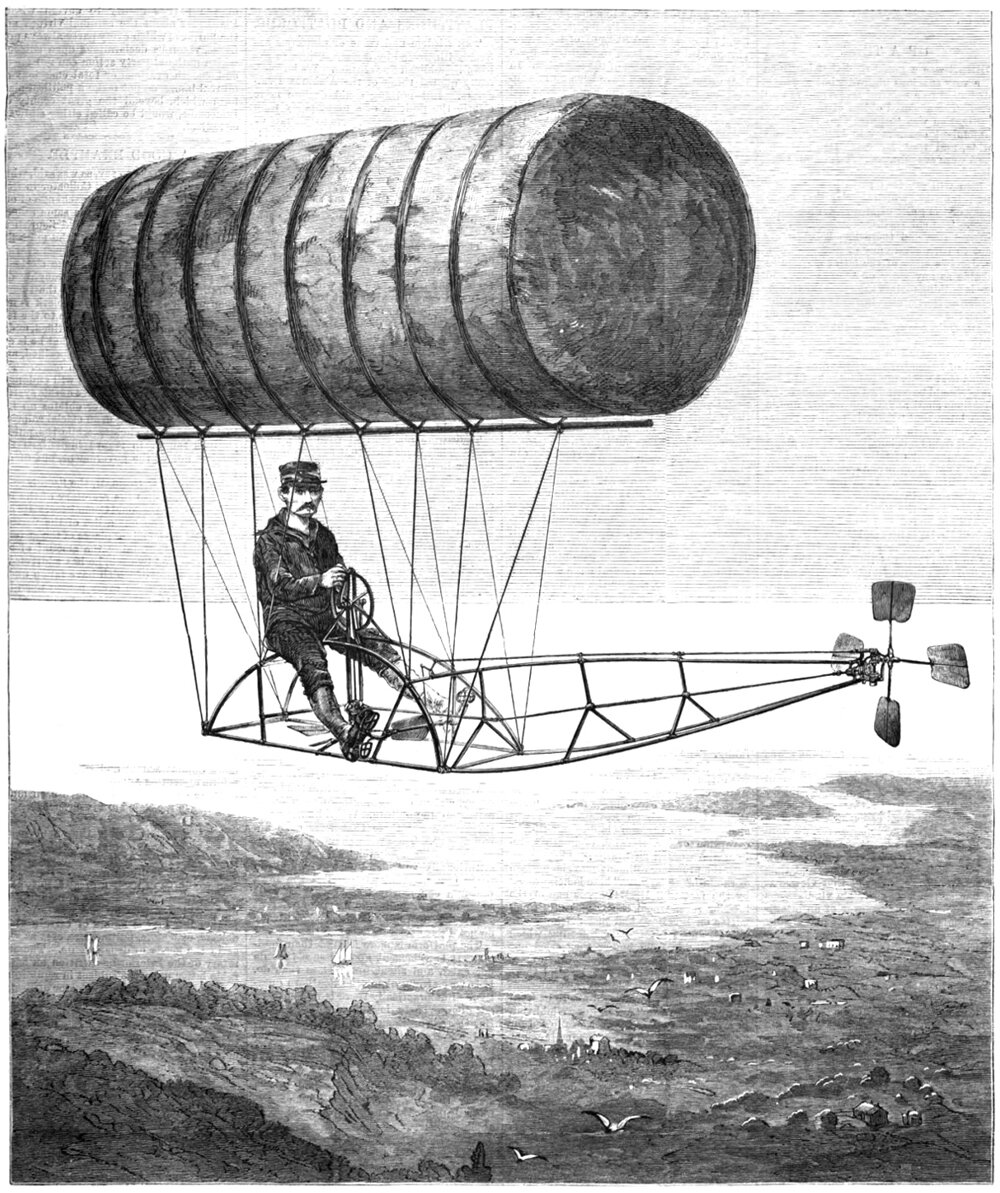
Charles F. Ritchel's Dirigicycle
This is the cover of Harper’s Weekly from July 13th, 1878. The issue featured an etching of a man sitting on a tubular frame, suspended high in the air by what looks like an elongated bail of hay. The man pictured is Charles F. Ritchel, and he’s piloting his design for a dirigible. A dirigible is an airship capable of being steered (it comes from the Latin word dirigere, which means ‘to direct’), and the bail of hay is in fact a bag of rubberized fabric called ‘gossamer cloth’, filled with hydrogen gas.
