Welcome to On Verticality. This blog explores the innate human need to escape the surface of the earth, and our struggles to do so throughout history. If you’re new here, a good place to start is the Theory of Verticality section or the Introduction to Verticality. If you want to receive updates on what’s new with the blog, you can use the Subscribe page to sign up. Thanks for visiting!
Click to filter posts by the three main subjects for the blog : Architecture, Flight and Mountains.

Terracing and the Green Machine
Making meaningful green spaces in high places
Two things that every human being needs are to escape the surface of the earth through Verticality, and to be around plants and vegetation. Ever since the beginnings of permanent shelter and architecture, humans have been attempting to escape the surface by creating and inhabiting high places. We’ve also been repeatedly trying to recreate the experience of the surface by linking these spaces with greenery.

Bologna Rising
Here's a forest of towers in the Italian town Bologna, from the early 20th century. These towers were built as extensions of private homes for wealthy families. Their exact purpose isn't quite clear, but most likely it was a combination of status symbols and as means of defense during uncertain times. The image is quite compelling, with the forest of needle-like towers poking out above the lower buildings of the town below.
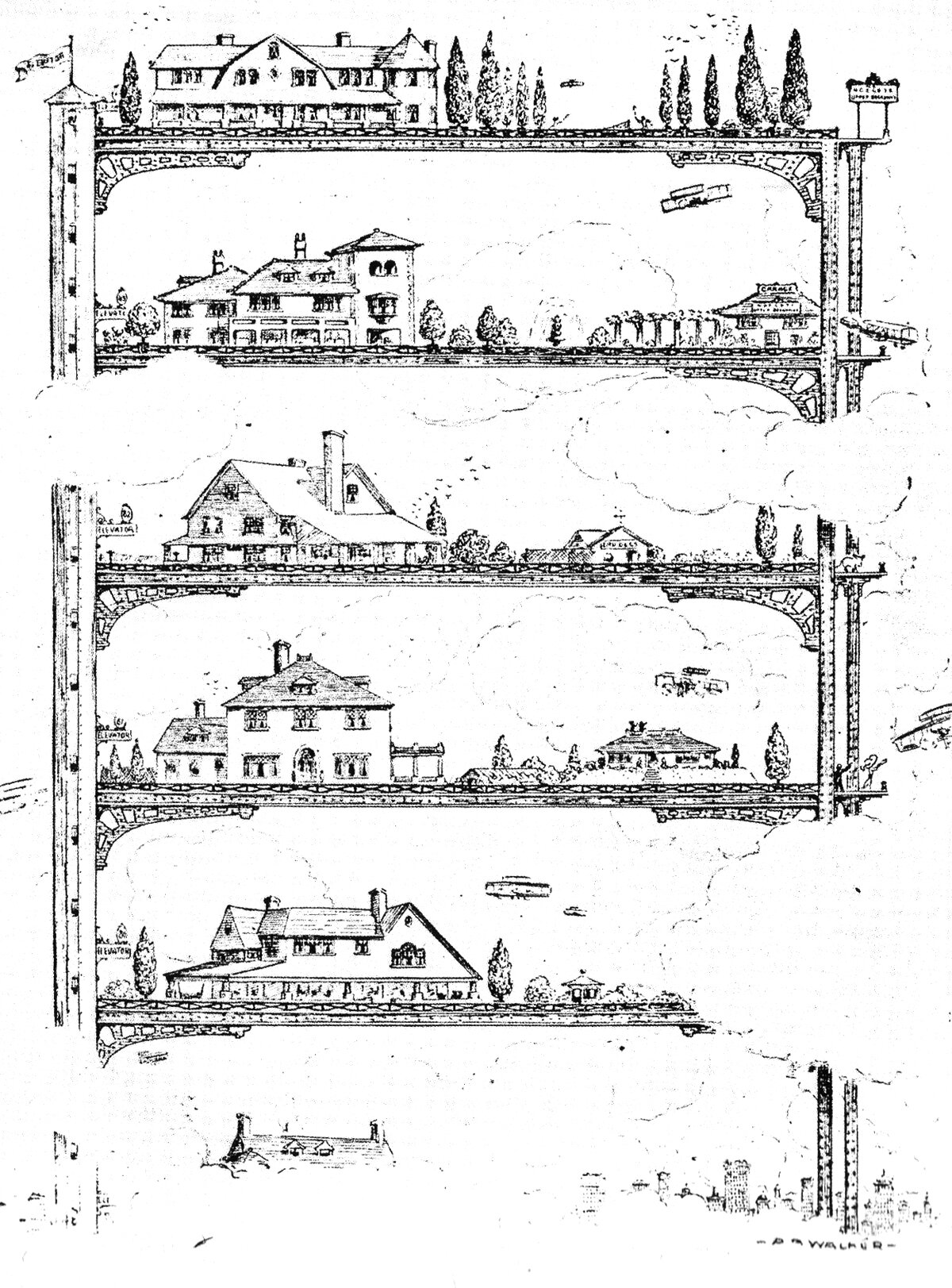
Stacking Suburbia
One of the major challenges with the high places we construct is that we're built for a surface-based existence. The surface is where the action is, and it's where our species has lived and evolved since before we colonized the world. Even the Ancient Romans called their six- to seven-story apartment buildings insulae, which is Latin for island, symbolizing the isolation that comes with living and working away from the surface. The advent of the modern skyscraper brought with it the possibility of living and working far, far away from the surface, which creates a special set of problems. How can we recreate the variety of the surface in the sky?

Man Vs. Nature
A bit of context can change many things. Take a look at this drawing, titled Man Vs. Nature from a 1925 edition of Le Petit Larousse Illustré. The graphic compares the tallest works of architecture at the time to major mountain peaks from nature. It's a reality check to consider the size of the Eiffel Tower in Paris, shown as a tiny speck on the bottom left of the image.

Verticality, Part IV: Beating the System
Homo Sapiens becomes the first animal to escape the food chain
Monkeys and apes are vulnerable creatures. Our source-code was built for a life in the trees, and on our own we lack any natural means of defending ourselves. Compared to other animals that evolved to survive on the savannah, we have no claws or fangs, we’re not particularly quick, and we don’t have natural camouflage. This makes us dangerously vulnerable to predators, and meant we needed to find another evolutionary niche in order to survive. Our answer was power in numbers.

Skylines As Value Indicators
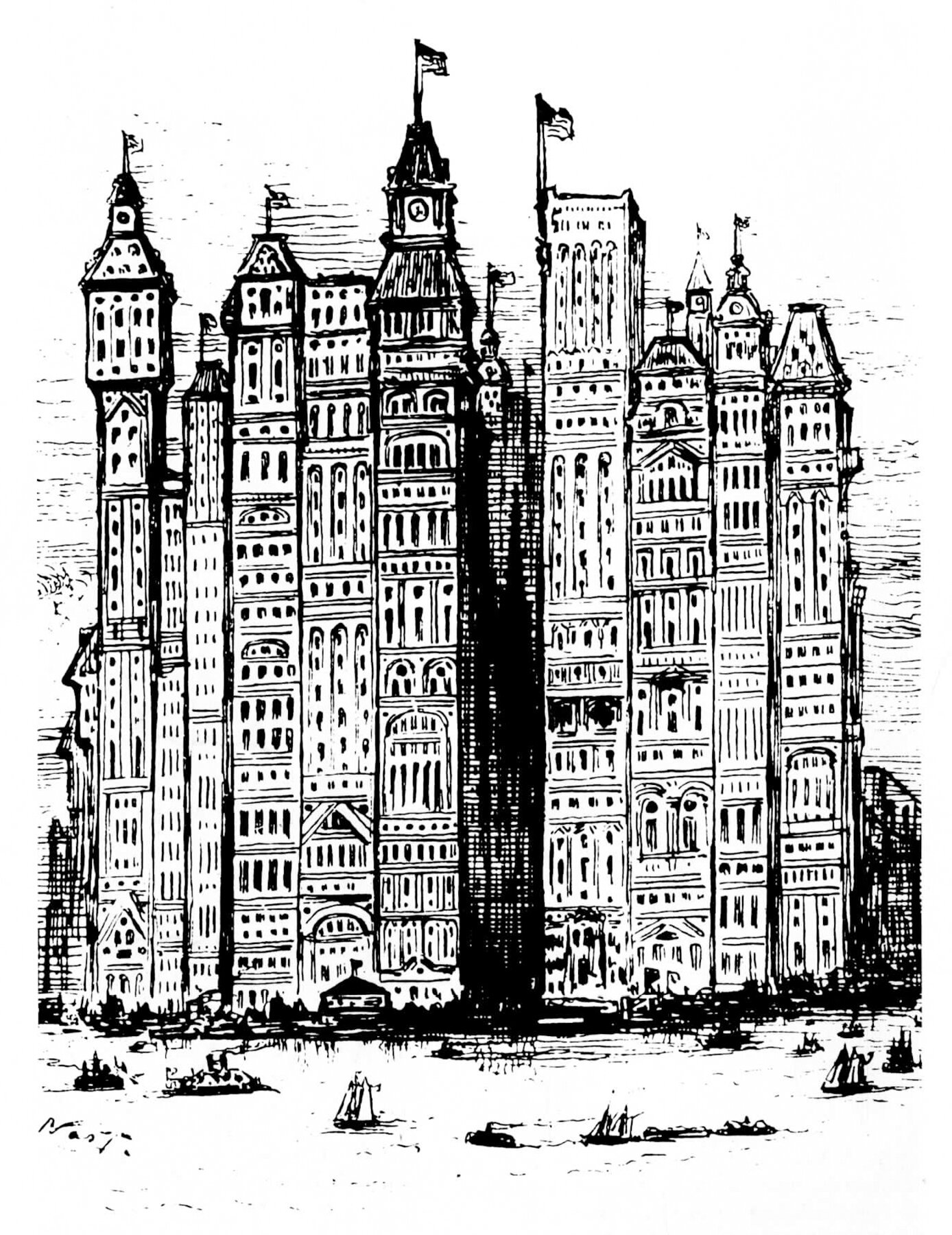
Take a look at this 1881 Cartoon by Thomas Nast for Harper’s Weekly titled New York A Few Years from Now. Nast shows the southern tip of Manhattan Island, jam-packed with a phalanx of skyscrapers. The buildings are pushed so close together it’s hard to imagine where the streets are. Back in the shadows, you can just make out the spire of Trinity Church, which at the time was the tallest building in the country. Nast is being hyperbolic, of course, but the reality of most modern cities isn't far off.
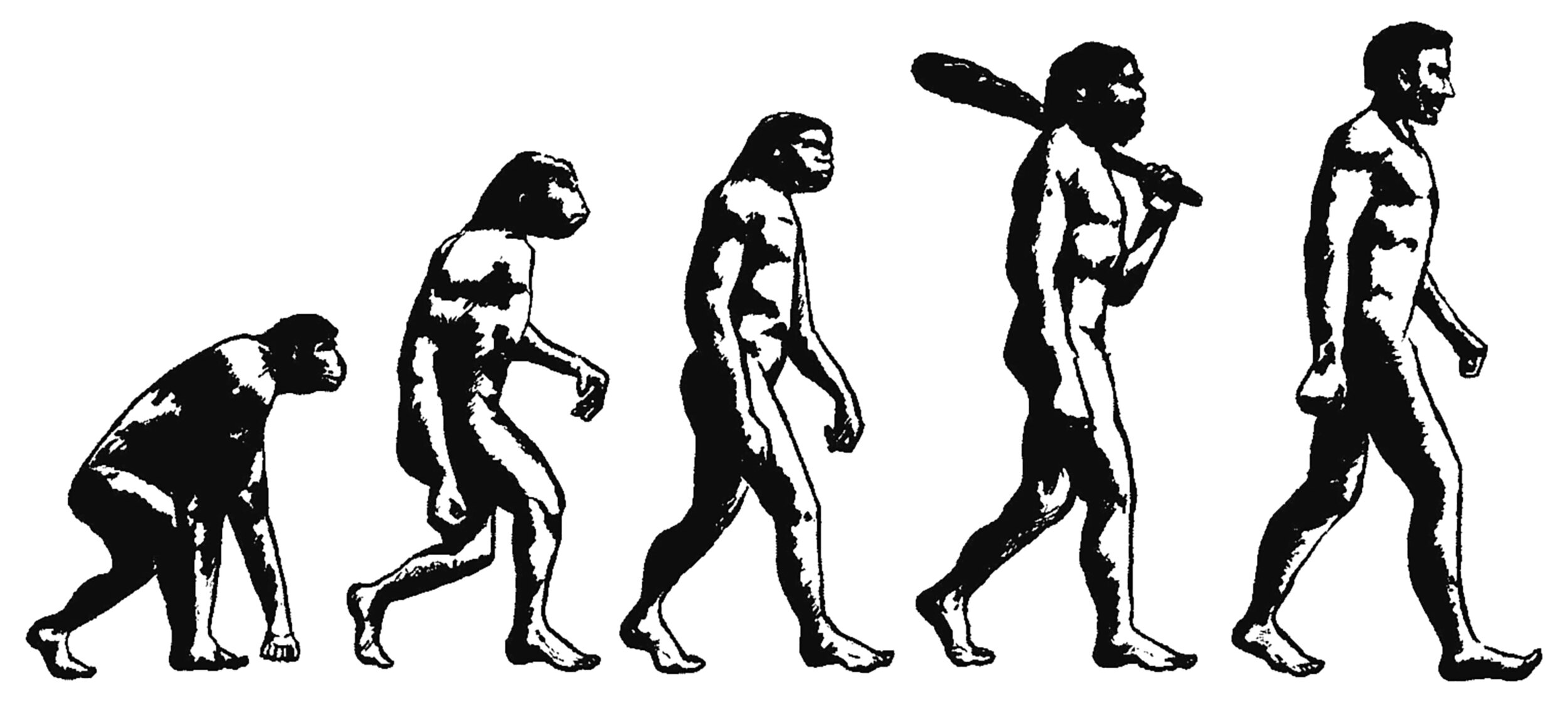
Verticality, Part III: Inception
Our first act of descension and our first act of ascension
Our species evolved within the context described in Part I, and our physical surroundings would provide the foundation for our struggles with Verticality, as described in Part II. These early struggles would be defined by two acts. The first is an act of descension: we came down from the trees and out onto the savannah to become surface-dwellers. We would still carry much of the baggage from tree-dwelling life with us, however. I’ll henceforth refer to this baggage as our source-code. The second is the shift to bipedalism, resulting in our upright, vertical bodies. Together, these two acts would set the stage for the future and our never ending struggle to escape the earth’s surface.
The Language of Verticality
Phrases and sayings that convey the natural vertical hierarchy in our everyday lives.
Height and Verticality are closely tied to language. We have many phrases and sayings that convey the natural vertical hierarchy in our everyday lives. These generally align with the idea that high equals positive or good and low equals negative or bad.
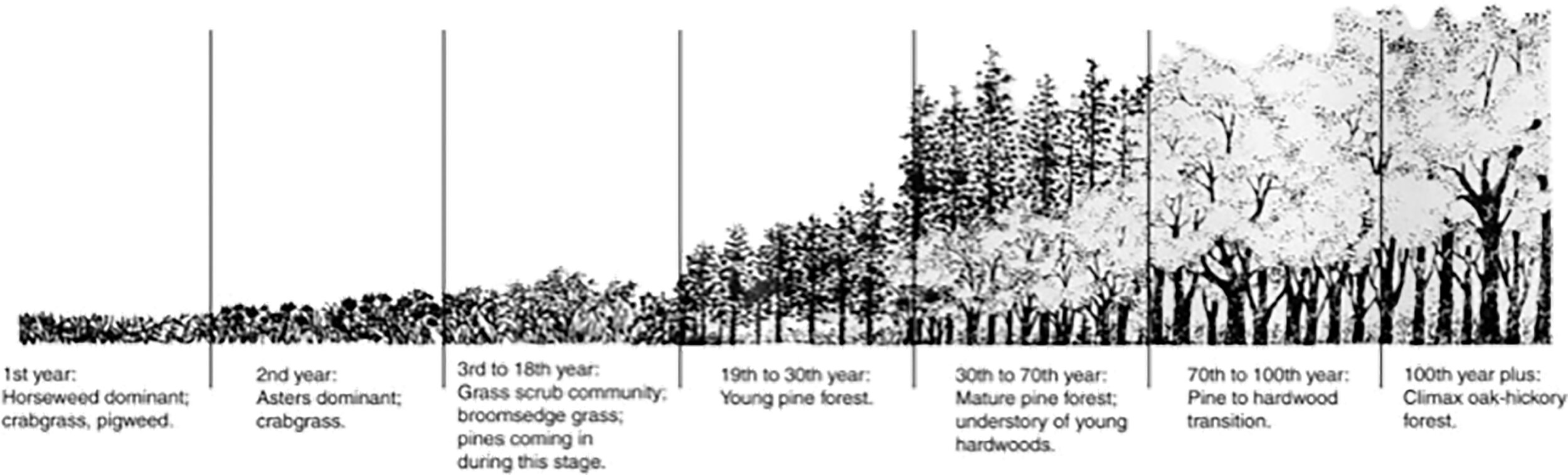
Verticality, Part II: The Seeds of Verticality
Natural phenomena throughout our context that exhibit verticality
So there we were. Confined to the earth's surface, competing with life around us and existing at the center of our own worlds. As our ancestors evolved in the trees, we didn’t have the means to shape our environment like we do today, so we had to look to the natural landscape of the earth’s surface to satisfy our need for Verticality and exploit them whenever possible. These natural phenomena would define our early relationship and struggles with the surface, the sky, and the underground.

High Places
Why do members of our species choose to climb mountains and seek out the highest places as a hobby or game? Seemingly, no other incentive exists other than the experience of being at the summit. As children, tree climbing and games like 'King of the Hill' illustrate our innate need to seek out the highest places for ourselves. Everywhere on the planet, high land is valued much more than low land, and those who 'occupy the high ground' nearly always have a distinct advantage over those who don't. Many of our most primitive towns and villages were located at high points in the landscape, and in modern cities, apartments or offices on the highest floors of buildings are the most coveted.

Verticality, Part I: The Context
The universal elements of our lives on planet earth
In order to understand how and why humans have an innate need to escape the surface of the earth, we must first examine the context in which we have evolved and existed throughout our history. This context is unchanging, and has been true for every member of our species who has ever lived. I’ll approach the subject in two parts.
