Welcome to On Verticality. This blog explores the innate human need to escape the surface of the earth, and our struggles to do so throughout history. If you’re new here, a good place to start is the Theory of Verticality section or the Introduction to Verticality. If you want to receive updates on what’s new with the blog, you can use the Subscribe page to sign up. Thanks for visiting!
Click to filter posts by the three main subjects for the blog : Architecture, Flight and Mountains.
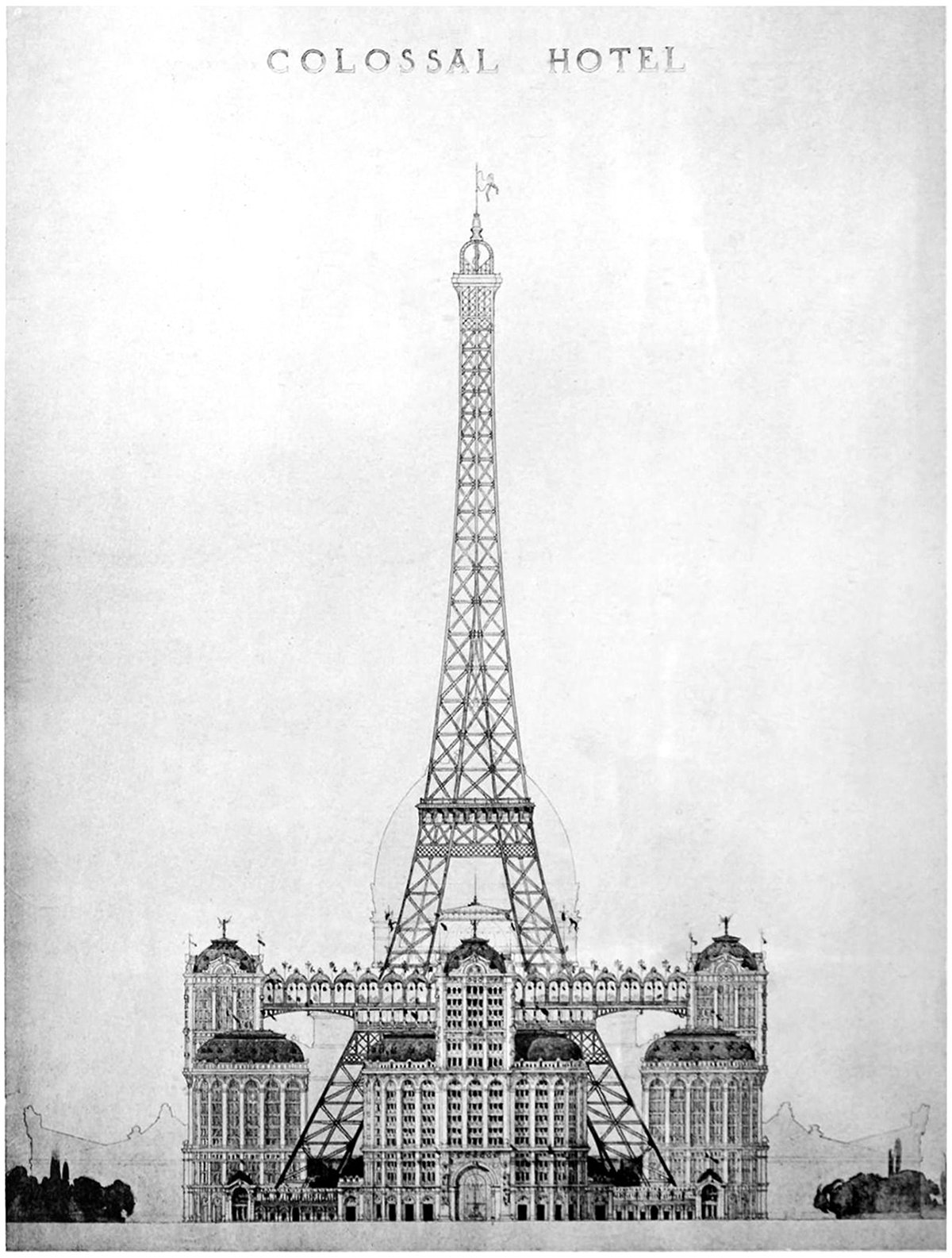
Alternate Realities : A Colossal Hotel at the Eiffel Tower
Pictured here is a proposal to put a colossal hotel at the base of the Eiffel Tower. It was proposed as part of the 1900 World’s Fair, called the Exposition Universelle, but it never got built. This elevation is the only drawing we have, which makes sense because most people who see the drawing would dismiss it immediately. The idea of filling up the void under the structure would destroy much of the Eiffel’s charm.
Eiffel as his Tower
Our buildings reflect our values and needs. This is especially true of our tall buildings, because they cost so much to build. When the Eiffel Tower was built in Paris, it reflected a worldwide drive for height in our buildings that was emerging at the time. It was a such a powerful statement of verticality that the man who designed it became something of a celebrity. He became linked with the tower in the eyes of the public, so much so that it was named after him like one of his children. This rarely happens with a building, but it demonstrates just how big an impact the Eiffel Tower had on the world.

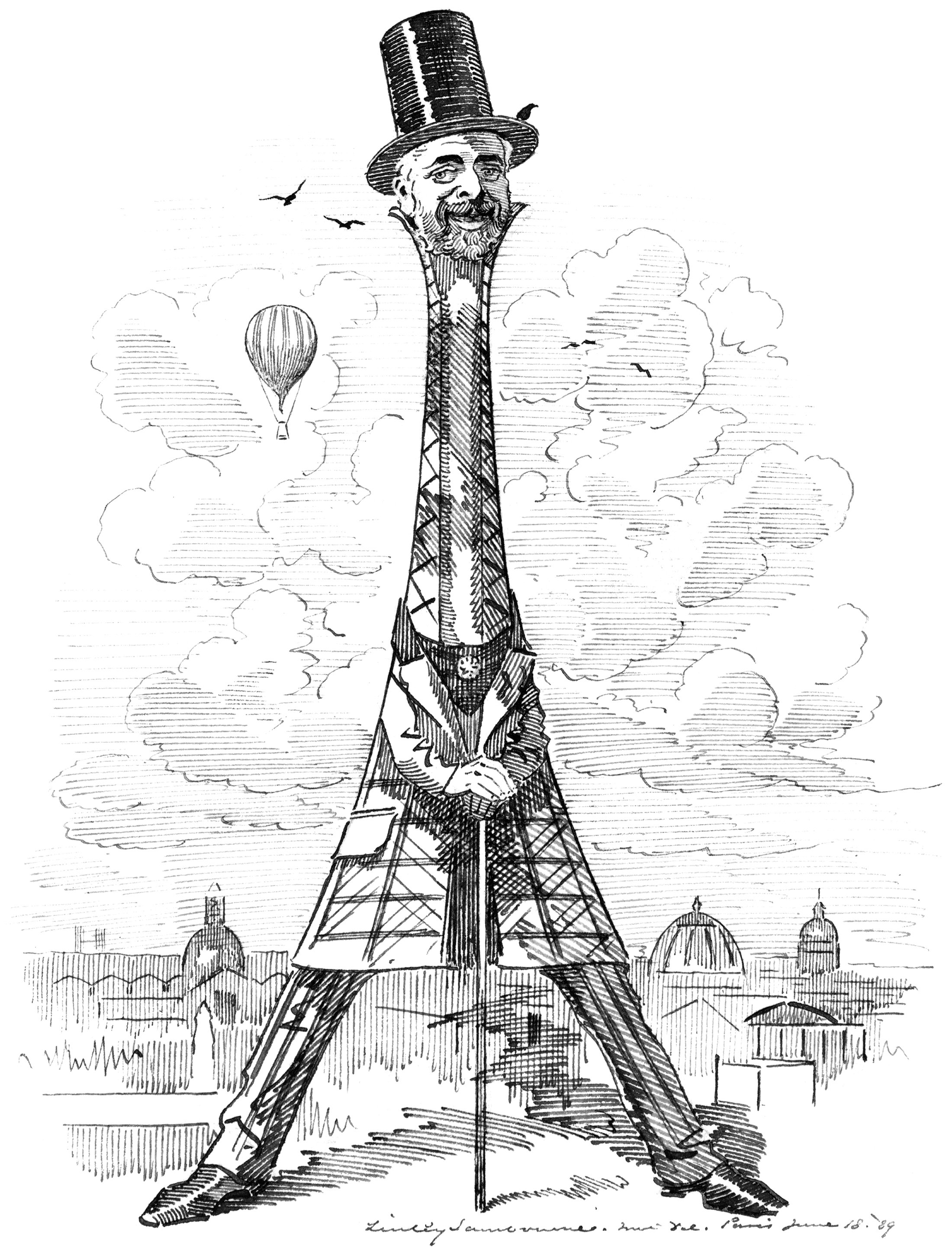
The Eiffel Tower Effect
When the Eiffel Tower was completed in 1889 for the World’s Fair in Paris, it changed the world. It re-defined what humans were capable of, and it gave the city of Paris an architectural icon that hasn’t faded with age. It was the tallest structure in the world, and it allowed its visitors to achieve verticality. As such, upon its completion the world took notice. Countless media sources reported on the structure, and it instantly took its place on the world stage. Pictured above is one such example of this. It’s an illustration from an 1889 issue of Punch magazine, and it shows a flock of birds flying toward the Eiffel Tower. These birds represent the countries of the world, and the piece was meant to symbolize the world’s envy for the iconic tower.

The Towering Centerpiece of an International World Centre
Pictured above is a monumental tower designed by Ernest Hébrard as part of a design for an international world centre. It was a visionary project without a real location, and I suspect it was either academic, or he designed it in order to make a name for himself as an architect and an artist. Either way, this tower was the centerpiece of a much larger plan, but it speaks volumes about Hébrard’s intent with the plan.
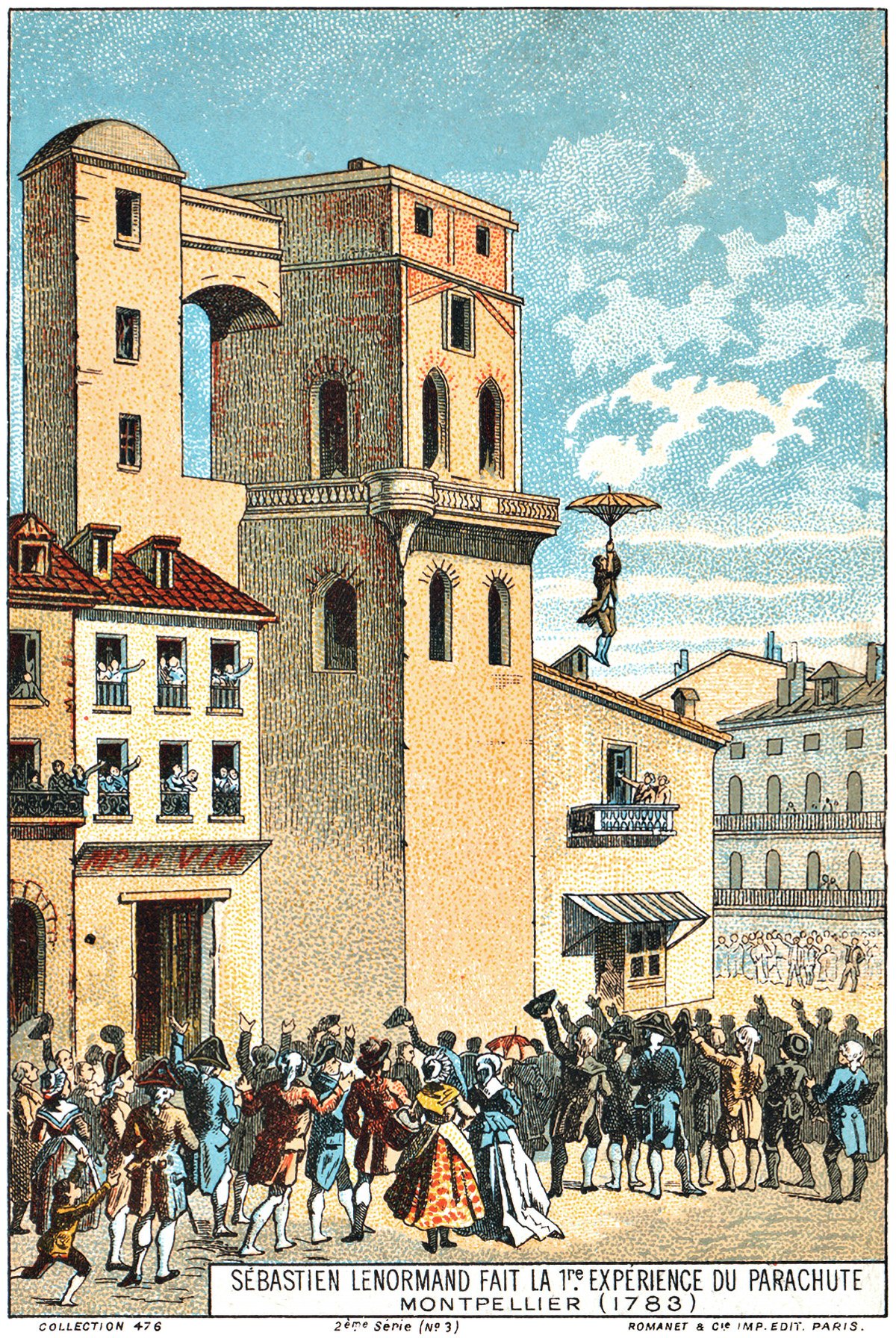
Sébastien Lenormand’s First Parachuting Attempt
Pictured above is a French illustration from 1890, showing Louis-Sébastien Lenormand leaping from a building with his parachute in Montpellier, France in 1783. He jumped from the Montpellier Observatory in front of a large crowd of onlookers who were hoping to witness the first-ever successful parachute demonstration. The caption reads Sébastien Lenormand Fait la 1re Expérience du Parachute, which means Sébastien Lenormand’s First Parachuting Attempt.
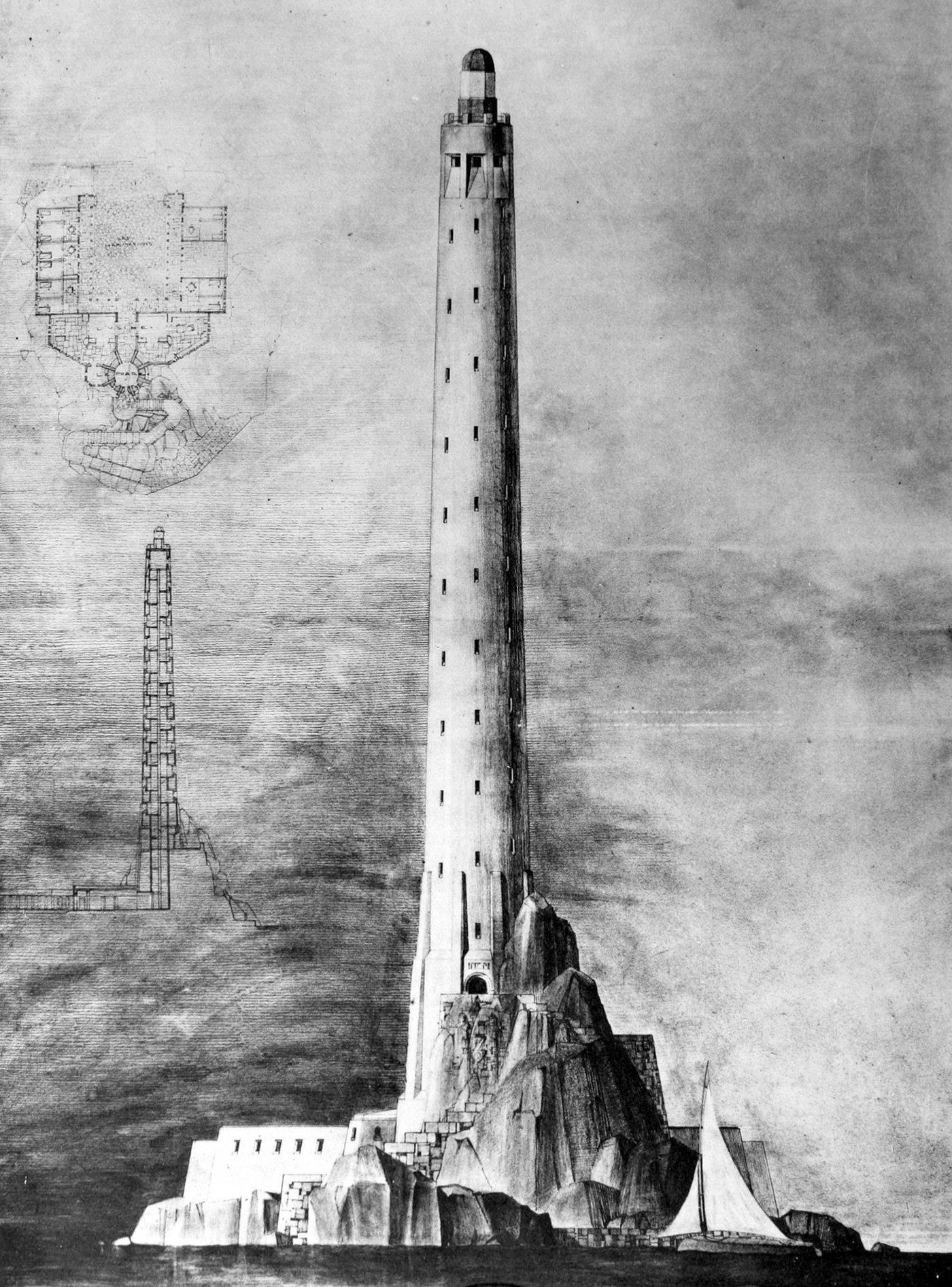
A Proposal for a Monumental Lighthouse
Pictured above is a student proposal for a monumental lighthouse from the École des Beaux-Arts. Designed in 1925, the structure is a tapered cylinder that rises high above the small, rocky island it resides on. As with any lighthouse, height is the main currency here. A higher light source will be visible from a greater distance, which makes the surrounding sea safer as a result.

A Foolproof Way to Direct the Balloons
The above illustration shows a comical scene involving a man suspended from a balloon being pulled by a pair of horses. It was drawn in 1787 and it’s titled Moyen Infaillible de Diriger les Ballons, or A Foolproof Way to Direct the Balloons. It’s meant to be a satirical take on ballooning at the time, when flight was front-and-center on the public stage. The characters in the scene are from commedia dell'arte, which is a type of theatre with recurring archetypal characters.
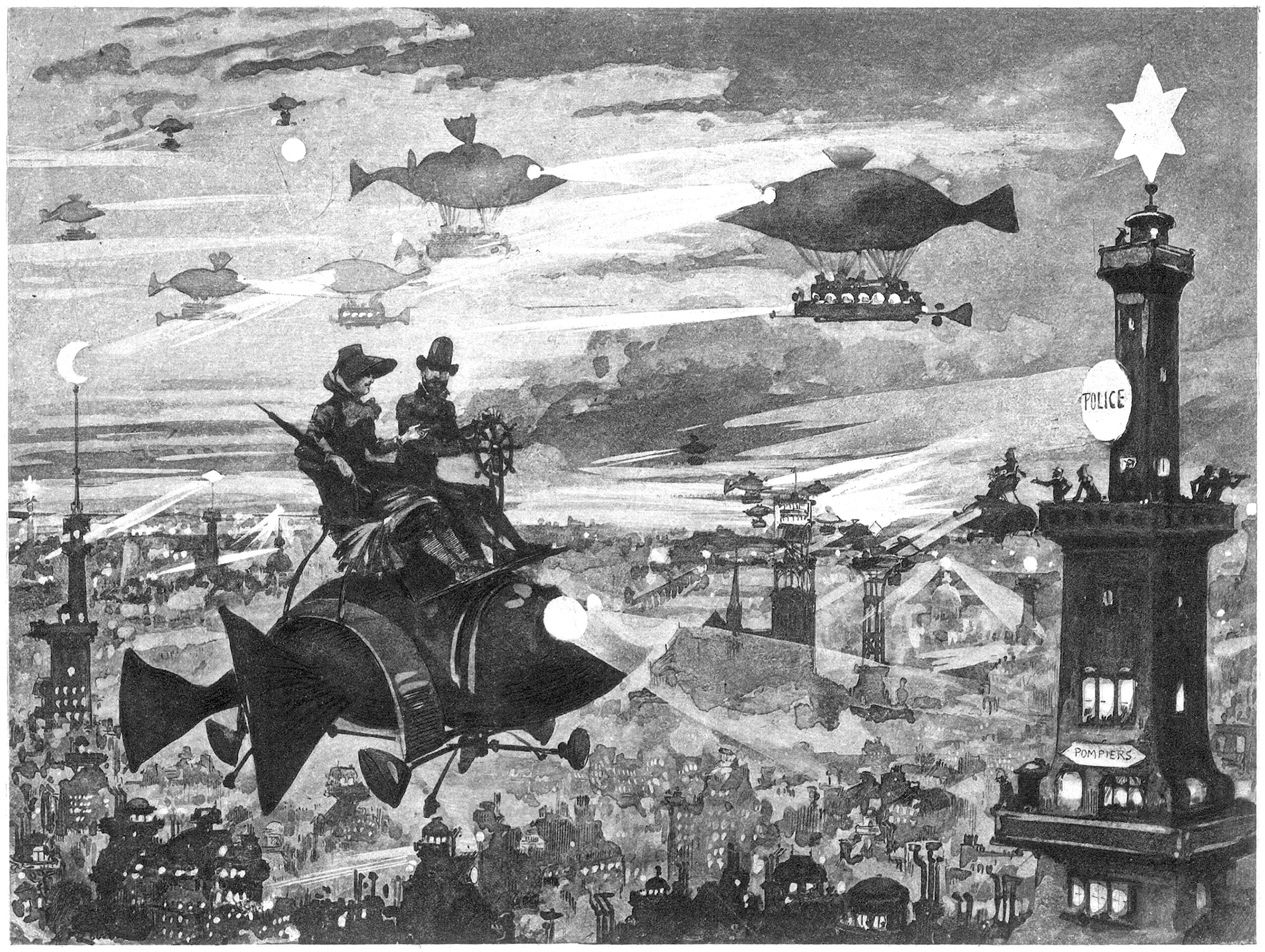

Albert Robida’s Vision for Paris
The above illustration was drawn by Albert Robida for his 1883 novel Le Vingtième Siècle, or The Twentieth Century. The novel describes a future vision for Paris in the 1950’s, focusing on technological advancements and how they would affect the daily lives of Parisians. Here he shows a vision for the night sky above Paris, which is dotted with various types of flying machines.
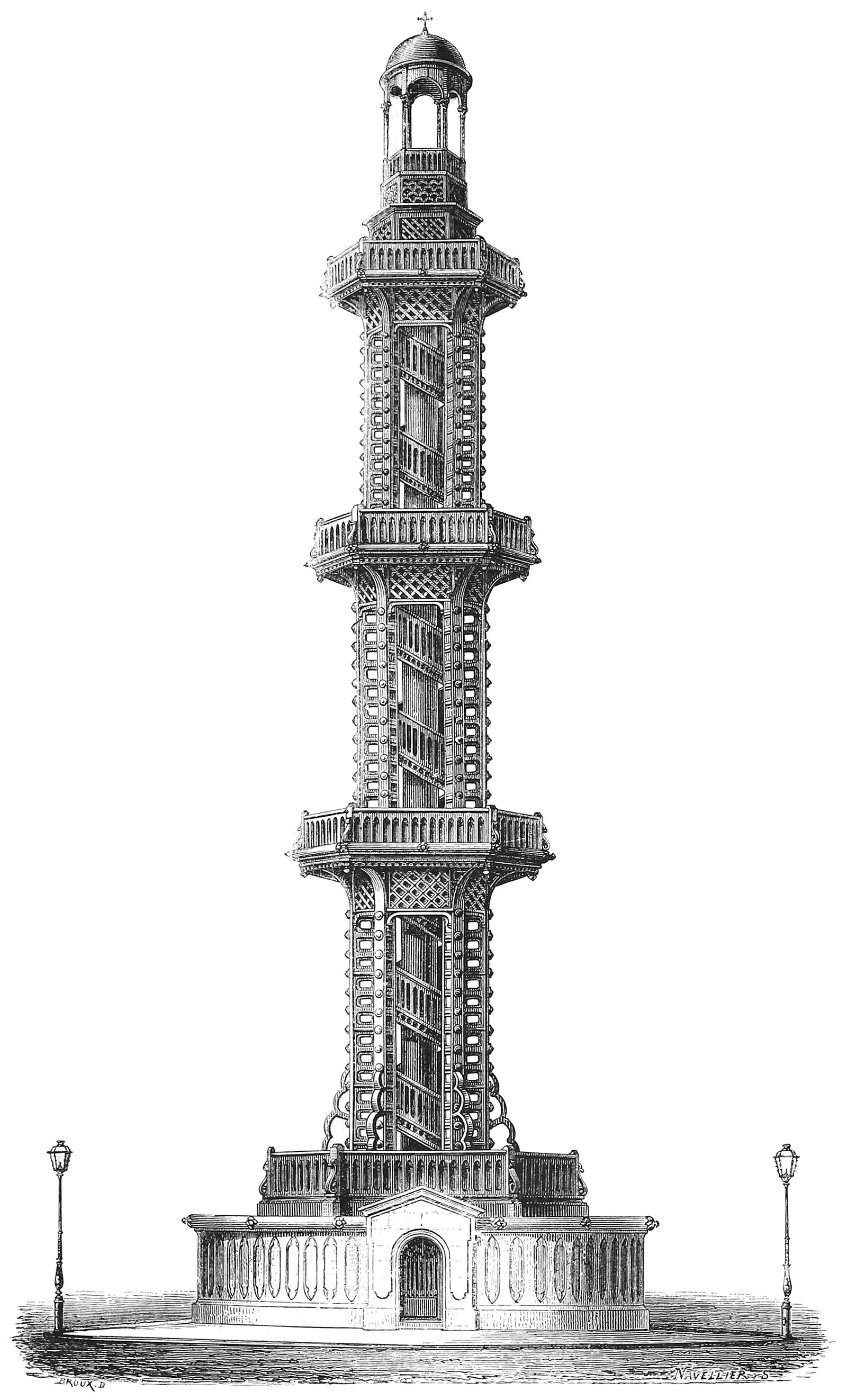
The Grenelle Artesian Well of Paris
Pictured above is the Grenelle Artesian Well in Paris, built from 1834 to 1841. During these seven years, an 8-inch diameter hole was drilled to a depth of roughly 550 meters (1,800 feet) below the earth’s surface. This process of construction took place far below ground, but in the end the well was marked with a 42 meter (138 feet) tower and fountain, placed a block away from the well itself. The tower was a deft mixture of uses, including a fountain, a sculpture, and an observation deck.

Utopian Flying Machines of the Previous Centuries
Pictured above is a French illustration from 1890, showing a collage of French flying machine ideas from the previous few centuries. The caption reads Les Utopies de la Navigation Aérienne au Siècle Dernier, which means The Utopia of Air Navigation in the Last Century. There are six flying machine ideas shown together in the sky.
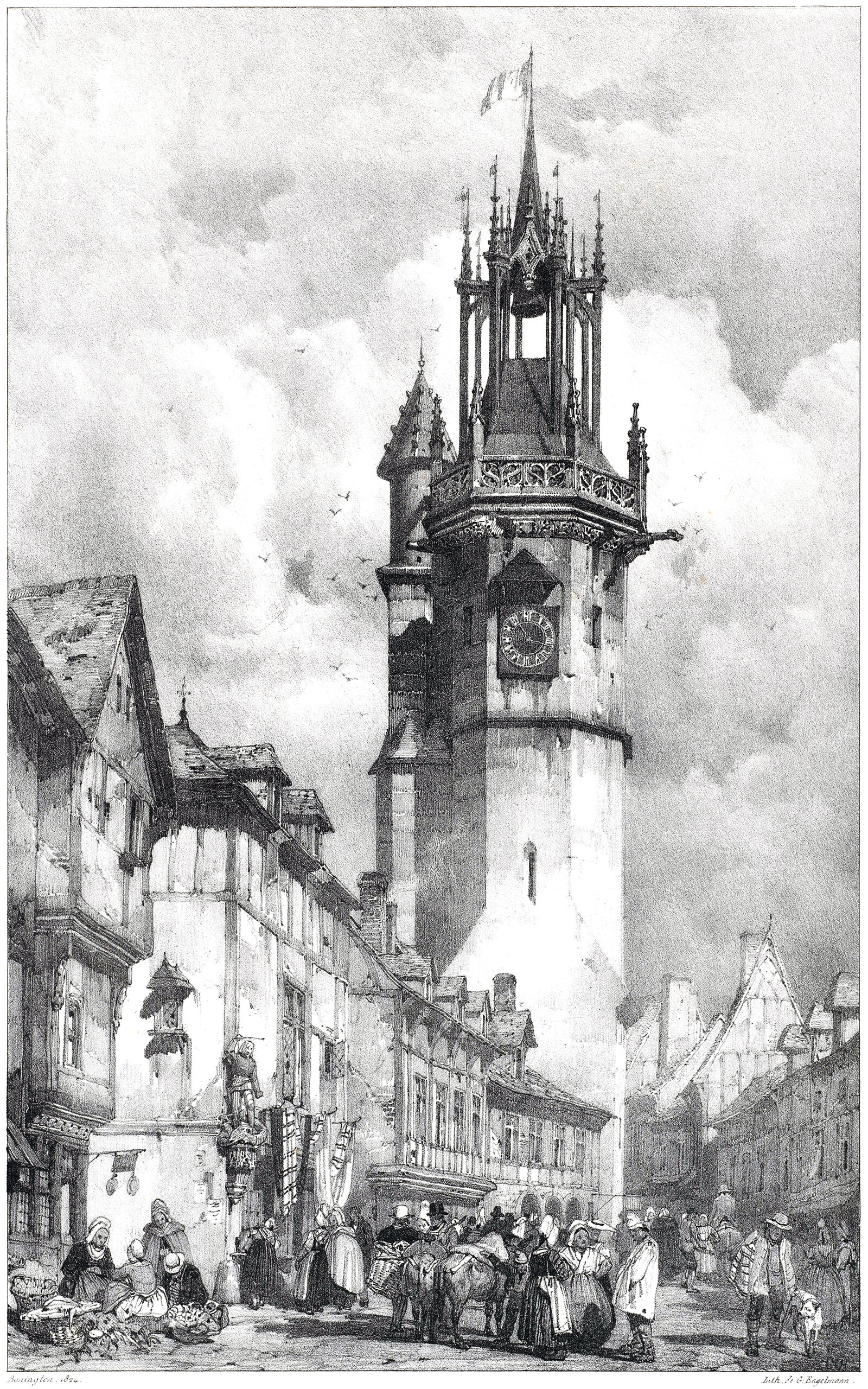

The Évreux Belfry
Pictured above is an illustration from 1825 showing a streetscape in Évreux, France. It was drawn by Richard P. Bonington, and it focuses on the town belfry, which was built from 1490-1497. Bonington does a great job of showing how a tower like this can dominate a streetscape, even if it isn’t that tall by today’s standards.
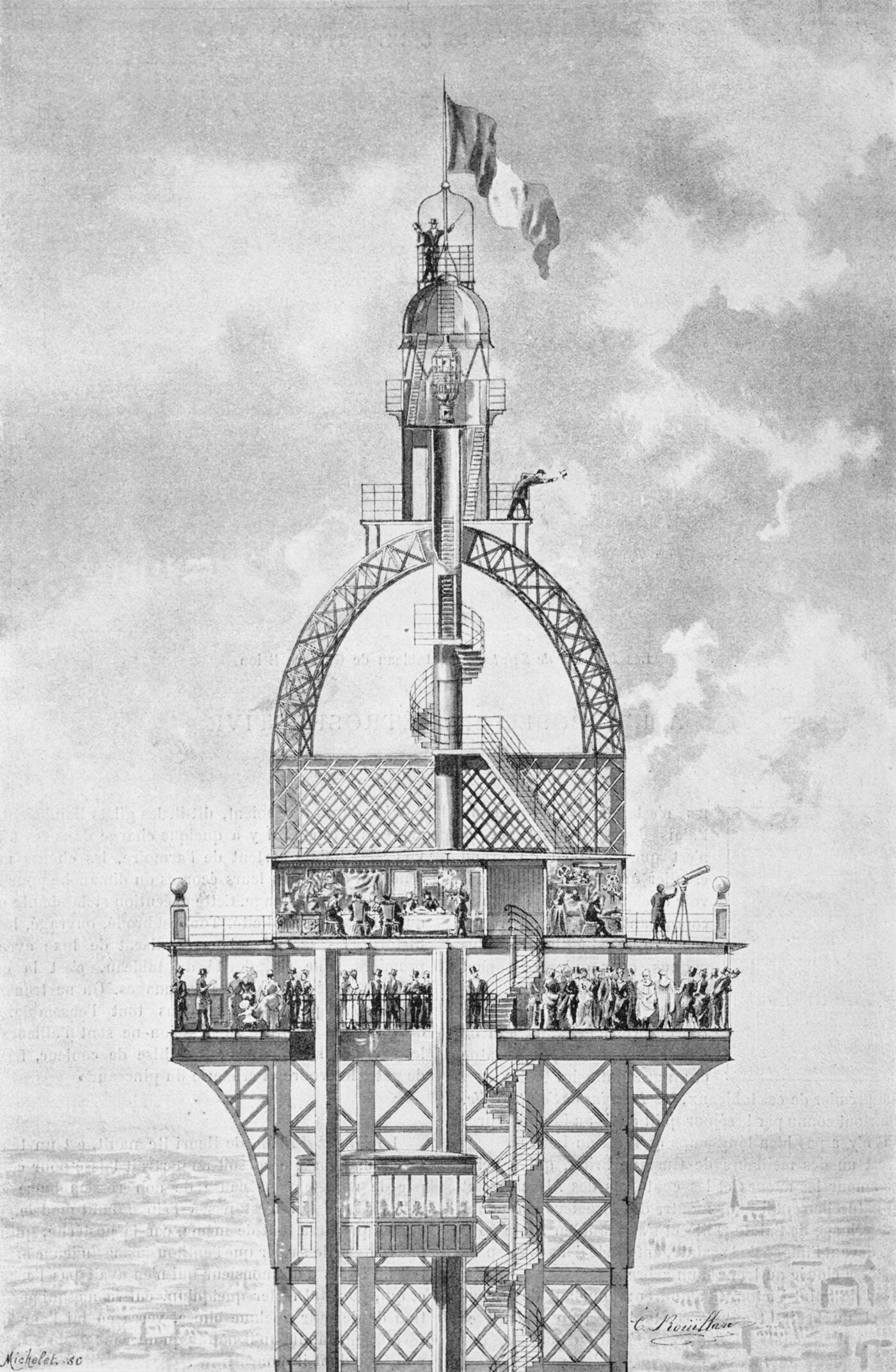
The Secret Apartment at the Top of the Eiffel Tower
Pictured above is an illustration of the Eiffel Tower’s original crown design. You can see the main observation deck, which is packed with people, all enjoying the view atop the tallest building in the world. Unbeknownst to them, however, is the private apartment located on the floor just above them. It was designed by and for Gustave Eiffel as a private space for himself to entertain notable guests and perform scientific experiments. It’s generally referred to as the secret apartment, but it was fairly well-known to the public that Eiffel built the space for himself.
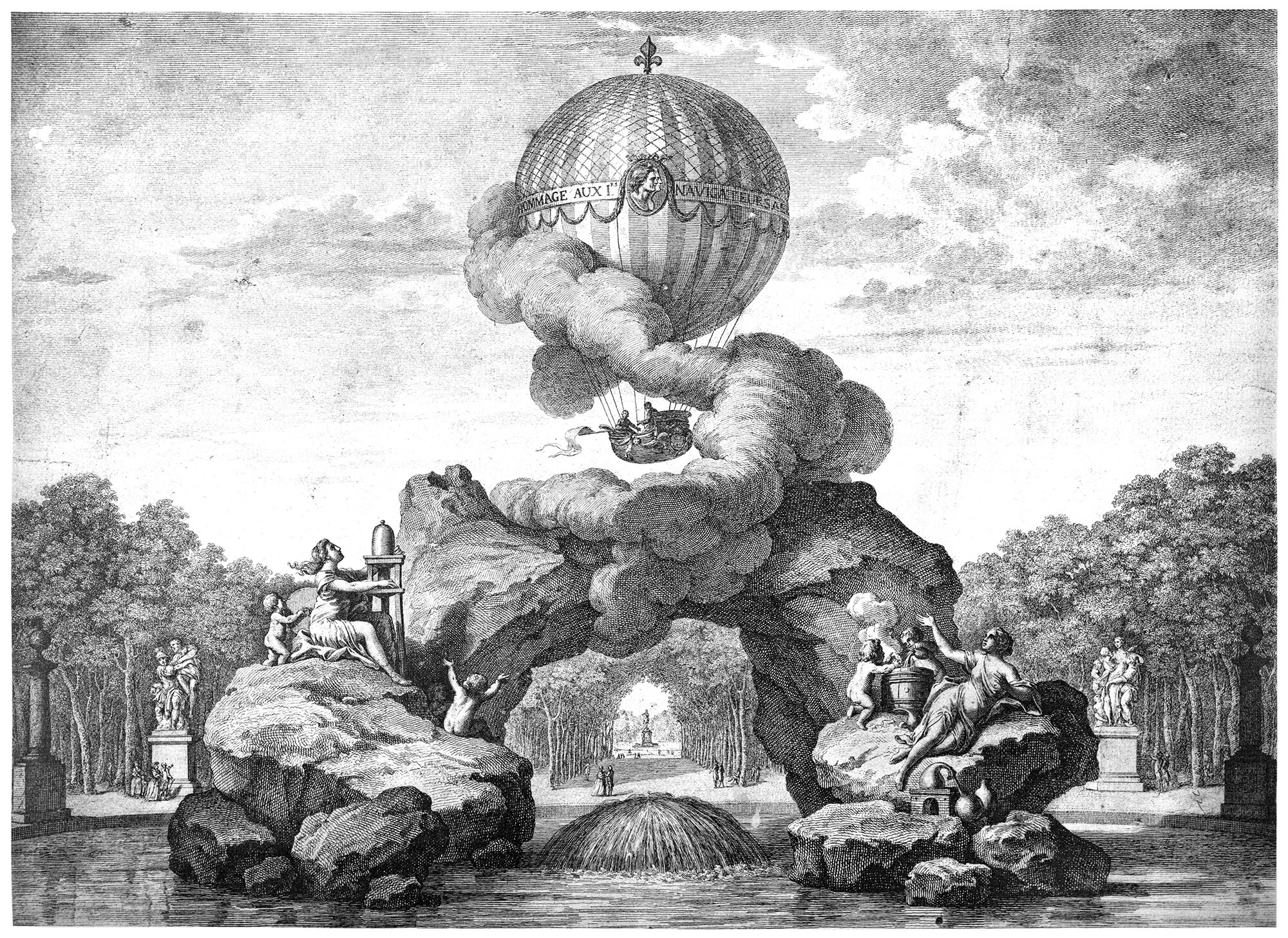

A Monument to the Glory of the First Aerial Navigators
Pictured above is the Projet d'un monument à la Gloire des Premiers Navigateurs Aériens, or the Monument to the Glory of the First Aerial Navigators. It was designed by an anonymous author for a site in the Tuileries Garden in Paris, and it consists of a stone arch placed in a fountain, with a balloon flying above it supported by a cloud-like form.
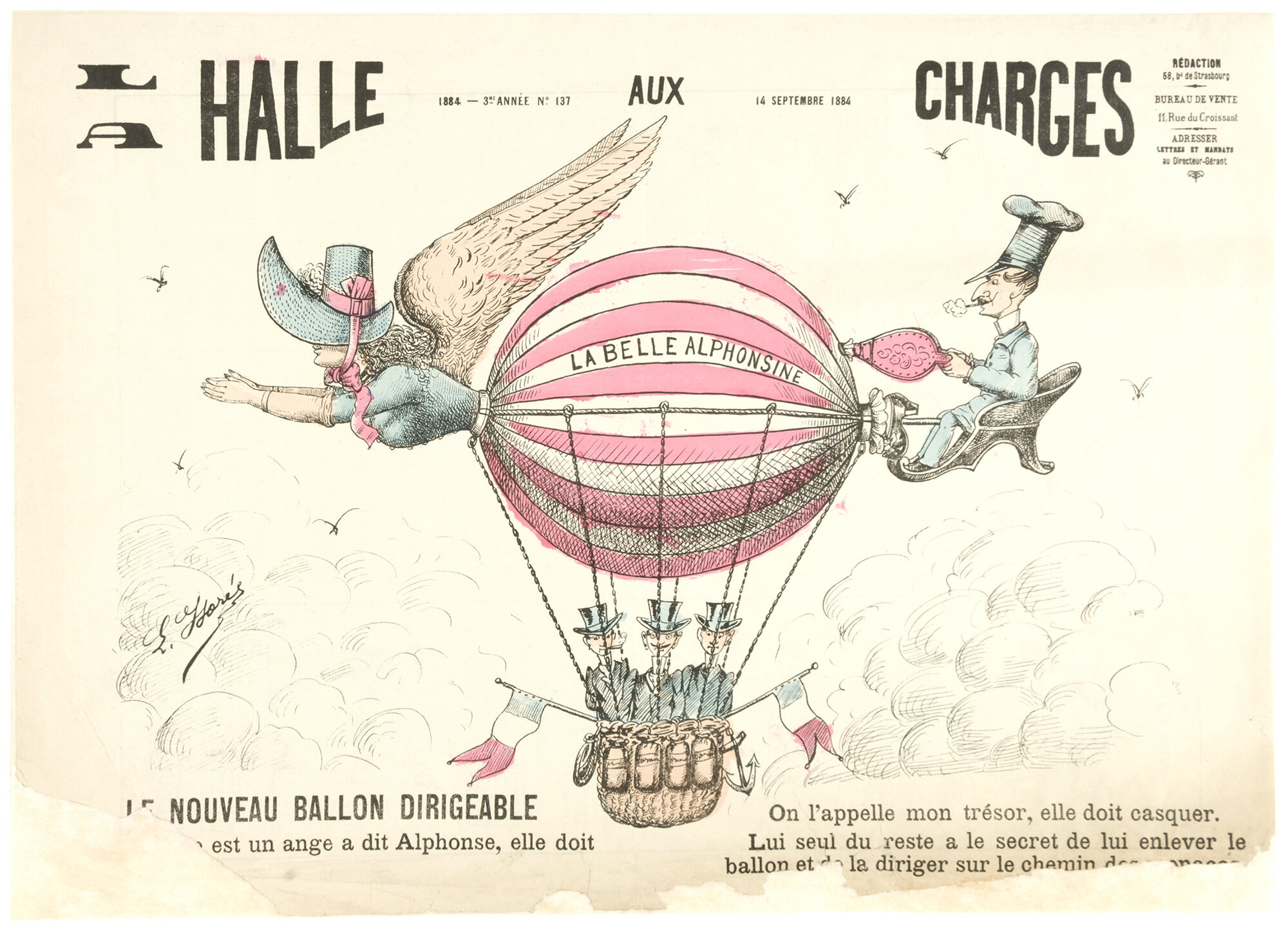
La Belle Alphonsine by E. Florés
In the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries, the human quest for flight was continuously on the public’s mind, and the above illustration is a testament to this. It’s from the front page of a French newspaper called La Halle aux Charges from 14 September 1884. This newspaper was well-known for it’s political caricatures and social commentary, and their choice to put a fictional balloon on their front cover is the perfect representation of what a successful flight means for all those involved.

By the size of the work, we measure the size of man
The above illustration is from the cover of an 1889 issue of Le Central. It shows a caricature of Gustave Eiffel standing in between his Eiffel Tower and the Great Pyramid. Inscribed on the pyramid is the phrase A la grandeur de l'oeuvre on mesure la grandeur de l'homme, or By the size of the work we measure the size of man. It’s a statement on verticality, and it illustrates how the height of these structures is their defining characteristic in the eyes of the public.
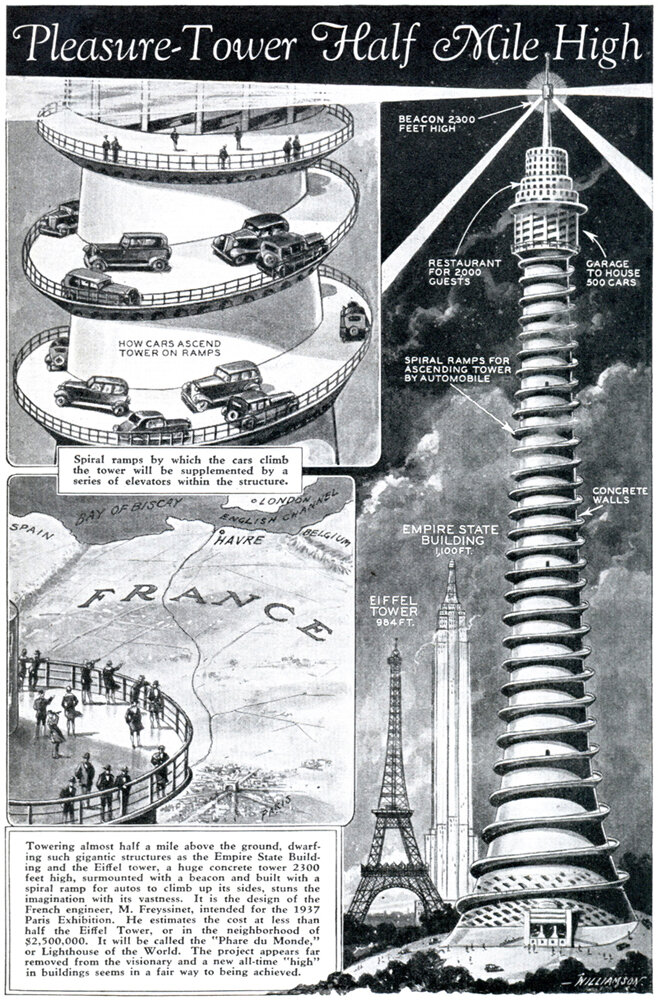
The Phare du Monde Pleasure Tower
Pictured above is a tower proposal from 1933 for the 1937 World’s Fair in Paris. It features an external spiral ramp leading to a parking garage 1640 feet (500 meters) from ground level.[2] Once at the top, visitors would find a restaurant, hotel and observation deck, and the spire contained a lighthouse beacon and a meteorological cabin. The view? Sublime. The design? Utterly ridiculous, unless taken as a satirical statement on civilization’s reliance on the automobile.
