Welcome to On Verticality. This blog explores the innate human need to escape the surface of the earth, and our struggles to do so throughout history. If you’re new here, a good place to start is the Theory of Verticality section or the Introduction to Verticality. If you want to receive updates on what’s new with the blog, you can use the Subscribe page to sign up. Thanks for visiting!
Click to filter posts by the three main subjects for the blog : Architecture, Flight and Mountains.
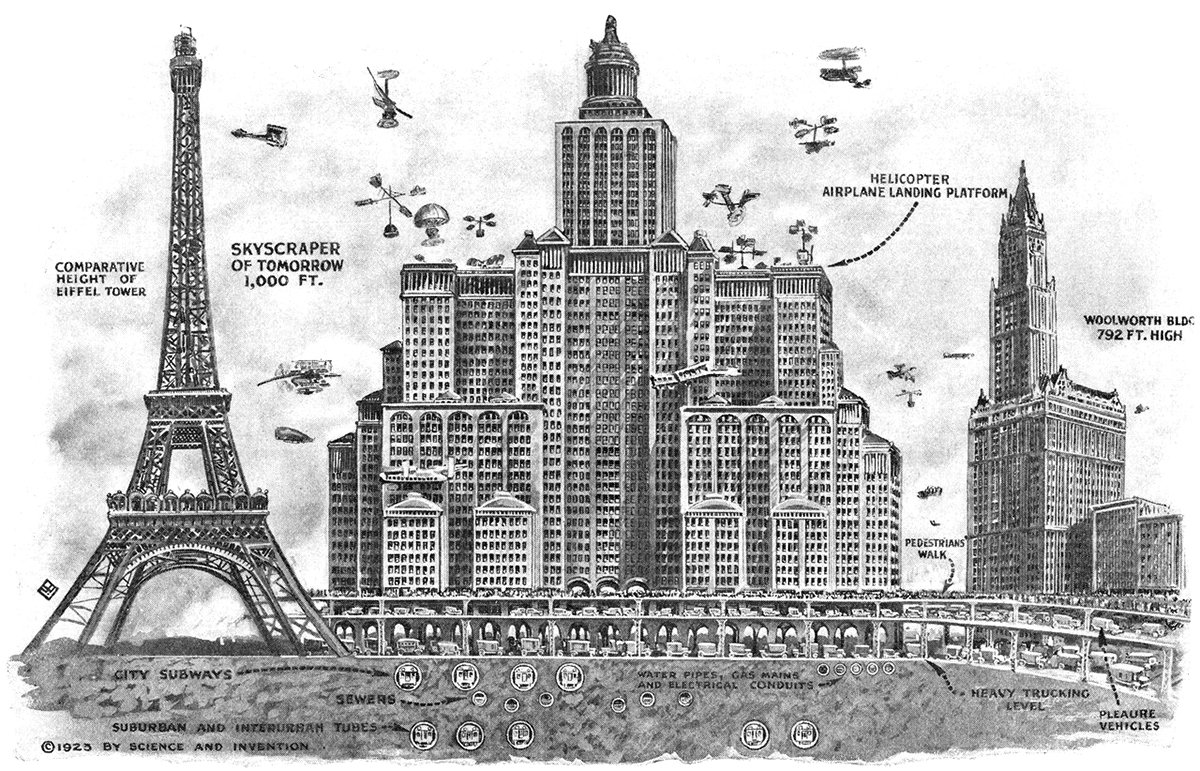
Skyscrapers of To-morrow
Pictured above is a 1923 illustration showing Harvey Wiley Corbett’s idea for a future skyscraper. Corbett believed buildings would continue to get taller and wider, resulting in massive, slab-like structures with aircraft landing platforms on their roofs and multiple underground levels of traffic. He compares his concept with two iconic buildings of the time, the Eiffel Tower and the Woolworth Building. These were both the tallest in the world when completed, which really hits home the sheer scale of Corbett’s structure.
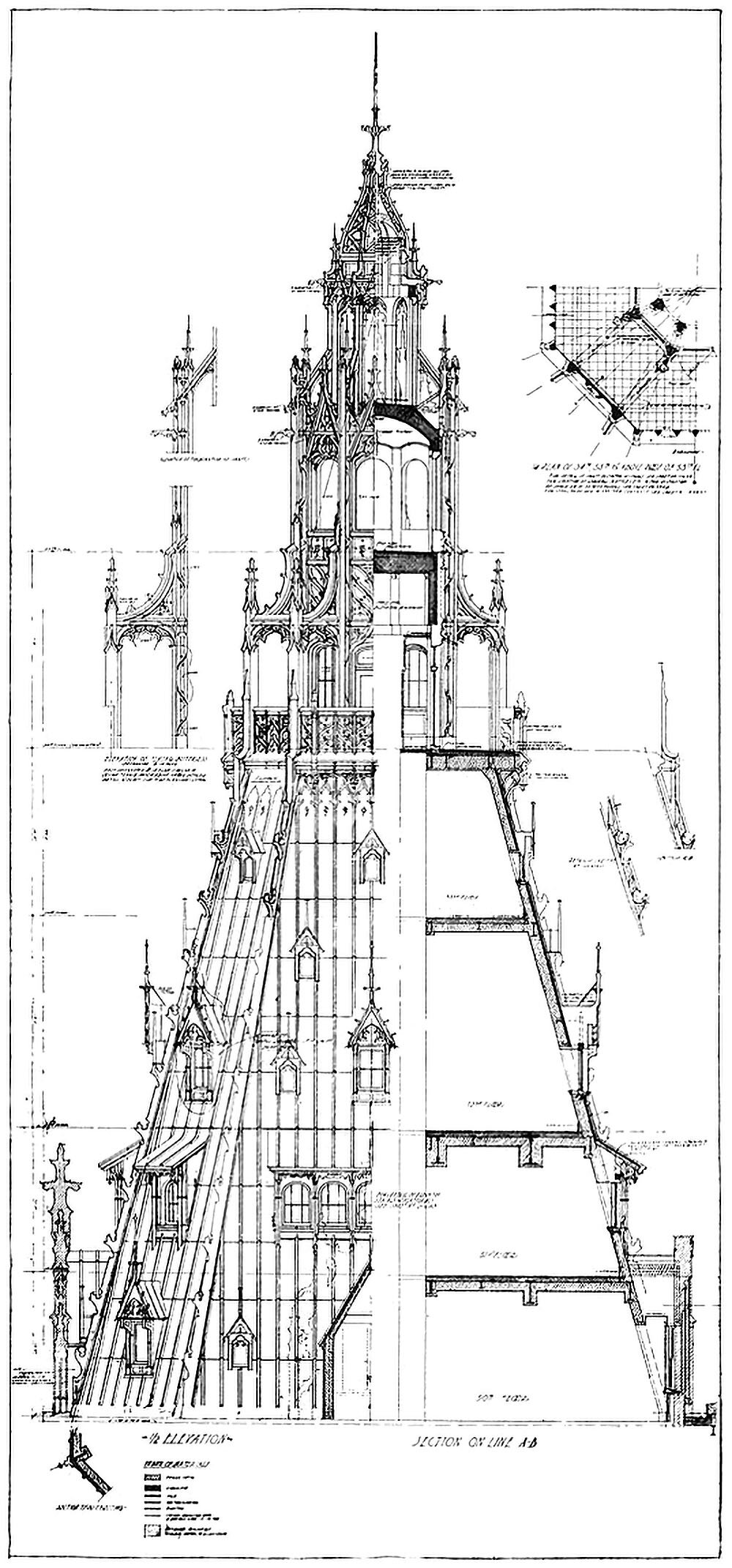
The Woolworth Building and the Question of Ornament
Pictured here is a combined elevation and section showing the crown of the Woolworth Building in New York City. Completed in 1912, the tower was the tallest building in the world at the time, and featured Neo-Gothic detailing throughout. As the drawing shows, this detailing is largely superficial, however. This is highlighted by the stark contrast between the left and right hand side of the drawing. This dichotomy between exterior and interior raises a couple questions related to verticality.
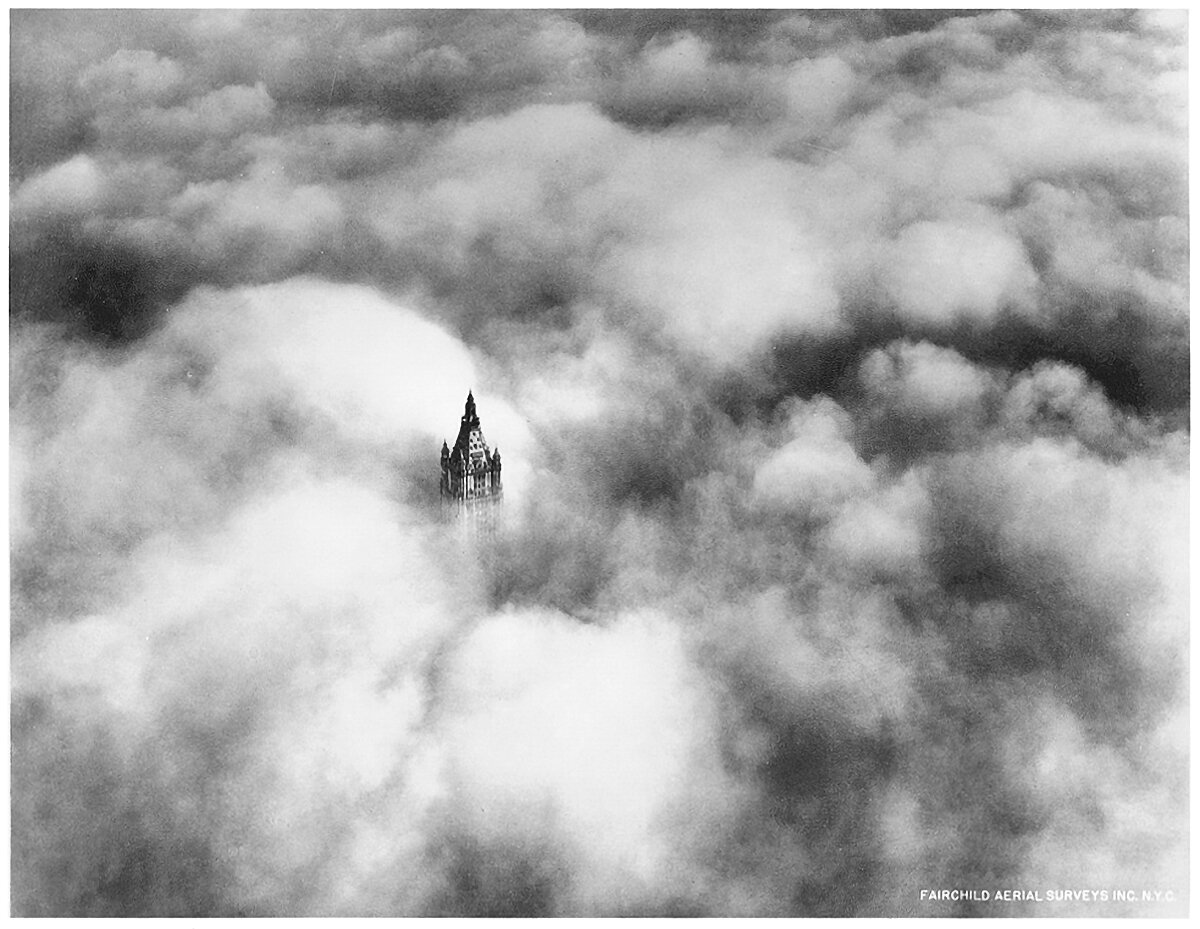

The Woolworth Building Tower Above the Clouds
The Woolworth Building was the tallest building in the world when it was completed in 1913. It towered above Lower Manhattan and dominated the skyline of the city. The above photograph was taken in 1928, and it shows the crown of the tower poking up through the clouds, inhabiting an otherworldly realm of sunlight and clouds. This is an iconic image, because it shows that buildings as tall as this achieve verticality for their occupants. On a day like this, the upper reaches of the building are truly in the sky.
“You don’t build [the world’s tallest] skyscraper to house people, or to give tourists a view, or even, necessarily, to make a profit. You do it to make sure the world knows who you are.”
-Paul Goldberger, American architecture critic, born 1950.

Verticality, Part X: Conquering The Skies
The construction of the Equitable Building in 1915 ushered in a new age of skyscraper design. Humans were now able to escape the surface of the Earth with our interior environments, and our need for Verticality had ceased to be driven by the unknown. It was now driven by our need to congregate through density and to distinguish ourselves from one-another. Ego had replaced God, and as a result our quest for Verticality would become synonymous with human achievement.

High Places
Why do members of our species choose to climb mountains and seek out the highest places as a hobby or game? Seemingly, no other incentive exists other than the experience of being at the summit. As children, tree climbing and games like 'King of the Hill' illustrate our innate need to seek out the highest places for ourselves. Everywhere on the planet, high land is valued much more than low land, and those who 'occupy the high ground' nearly always have a distinct advantage over those who don't. Many of our most primitive towns and villages were located at high points in the landscape, and in modern cities, apartments or offices on the highest floors of buildings are the most coveted.
