Welcome to On Verticality. This blog explores the innate human need to escape the surface of the earth, and our struggles to do so throughout history. If you’re new here, a good place to start is the Theory of Verticality section or the Introduction to Verticality. If you want to receive updates on what’s new with the blog, you can use the Subscribe page to sign up. Thanks for visiting!
Click to filter posts by the three main subjects for the blog : Architecture, Flight and Mountains.
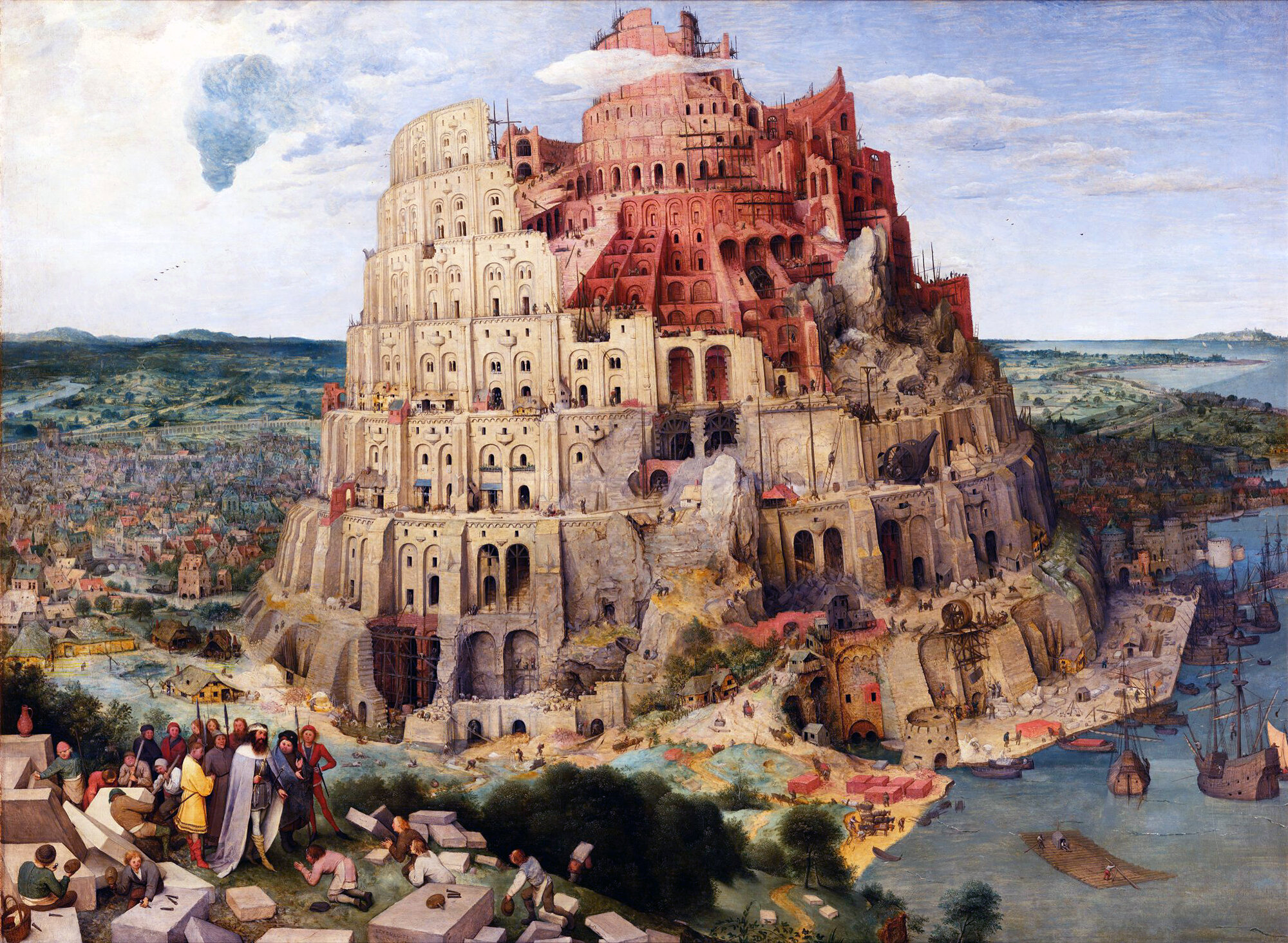

The Tower of Babel : A Parable of Verticality
The Tower of Babel is arguably the most storied myth about the human need for Verticality that has survived from antiquity. It’s a legendary tale of a clash between Ego and God, and it acts as a starting point for any worthwhile history of human towers or skyscrapers. Let’s take a look at why it’s been so influential, and why it encapsulates our struggles with Verticality.
“It is impossible that men should be able to fly craftily by their own strength.”
-Giovanni Alfonso Borelli, Italian physiologist and mathematician, 1608-1679.
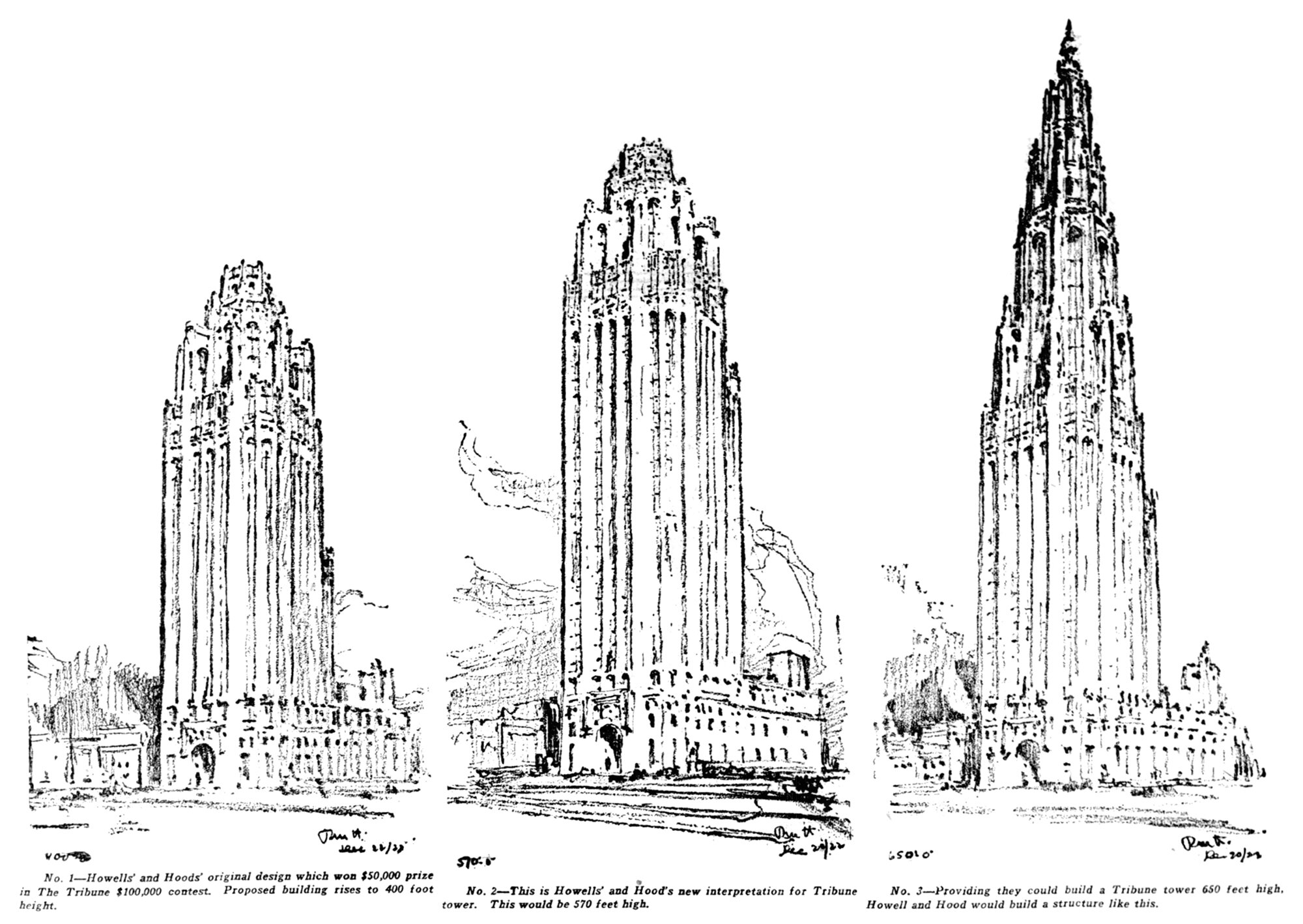
Alternate Realities : Chicago Tribune Tower
Pictured above are three design sketches for the Chicago Tribune Tower. They were drawn after the newspaper asked the architect to study taller options for the building, because they were considering whether or not to build the world’s tallest skyscraper. The increased height would require special approval from the city, so in the end they opted for beauty over height, and didn’t pursue the taller options.

Pierre Ferrand’s Corkscrew Airship
This is Pierre Ferrand de Montfermeil’s 1835 design for an airship, featuring a giant screw mechanism and an elaborate system of fins. Unfortunately details of the design are scarce, and this appears to be the only image we have. According to the authors of the book L’Aéronautique des origines à 1922, it originallt appeared in a brochure titled Projet pour le Direction de l'Aérostat par les Oppositions Utilisées, or Project for the Direction of Airships used by Oppositions.
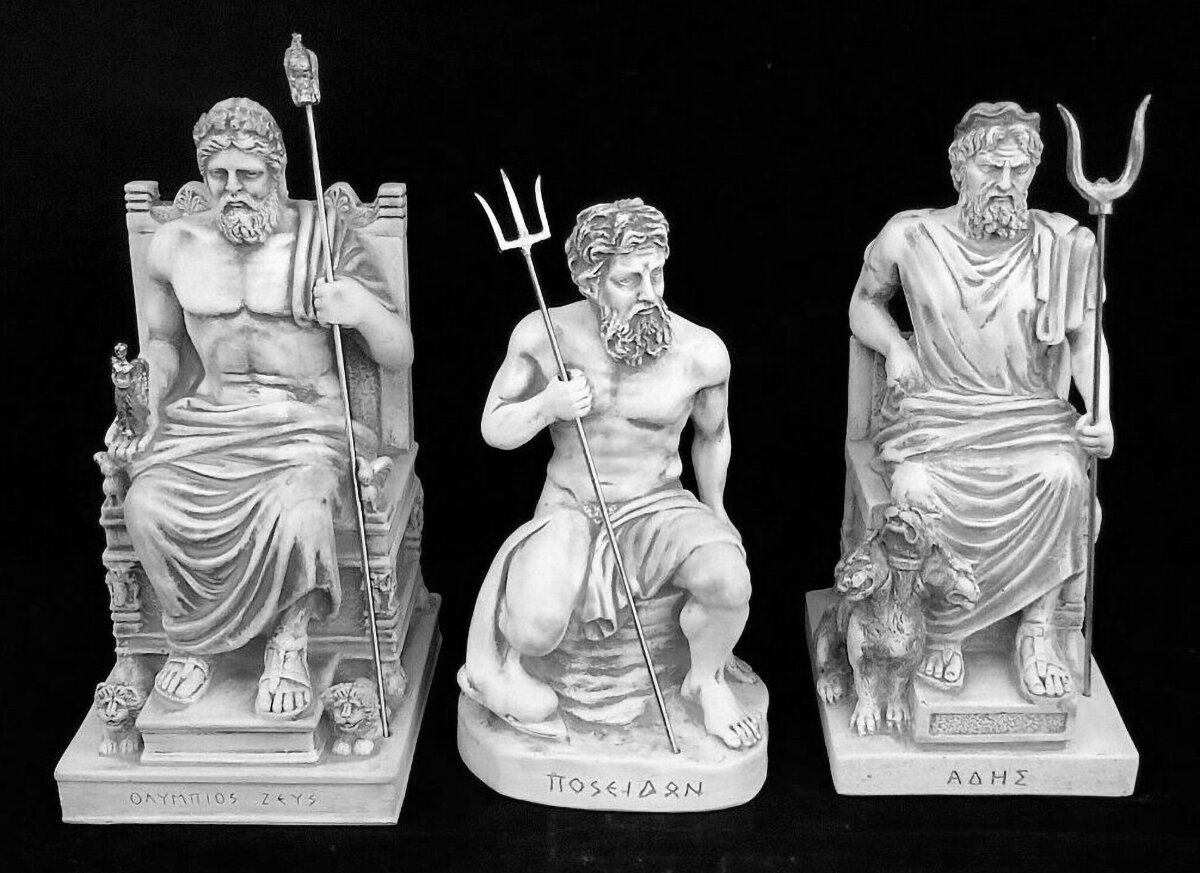

Zeus, Poseidon and Hades : The Verticality of the Greek Gods
Nearly all ancient belief systems are based on the surface, the underground, and the sky in some way. These three concepts represent something primal for humans, and throughout history we’ve attached myriad meanings and stories to the relationship between them. Typically, they’re either represented by an abstract concept or a god. An example of the former is the Christian idea of heaven and hell. An example of the latter is the Ancient Greek gods Zeus and Hades.
“A greater fear I do not think there was ... when I perceived myself on all sides in the air, and saw extinguished the sight of everything but the monster.”
-From The Divine Comedy, by Dante Alighieri, Italian poet and philosopher, 1265-1321.

Zoning Envelopes and the New York Skyscraper
Back in architecture school, I had a professor once say that the most effective way to create change is to adjust the building code. That way every architect must conform their designs to meet the code’s requirements, which is much more impactful than any single building could ever be. It was sage advice, and throughout the history of skyscrapers, it rings true. Throughout the history of skyscrapers, arguably the most influential of these changes occurred in 1916 in New York City.

By the size of the work, we measure the size of man
The above illustration is from the cover of an 1889 issue of Le Central. It shows a caricature of Gustave Eiffel standing in between his Eiffel Tower and the Great Pyramid. Inscribed on the pyramid is the phrase A la grandeur de l'oeuvre on mesure la grandeur de l'homme, or By the size of the work we measure the size of man. It’s a statement on verticality, and it illustrates how the height of these structures is their defining characteristic in the eyes of the public.

The Unpretentious Philosopher
Check out the above illustration. It’s the frontispiece to Louis Guillaume de La Follie’s science-fiction work La philosophe sans Pretention, or The Unpretentious Philosopher, from 1775. What’s most interesting about it is the flying machine featured in the drawing, evidenced by the crowd of onlookers in awe of it.
“Mechanical wings allow us to fly, but it is with our minds that we make the sky ours.”
-William Langewiesche, American journalist and aviator, born 1955.
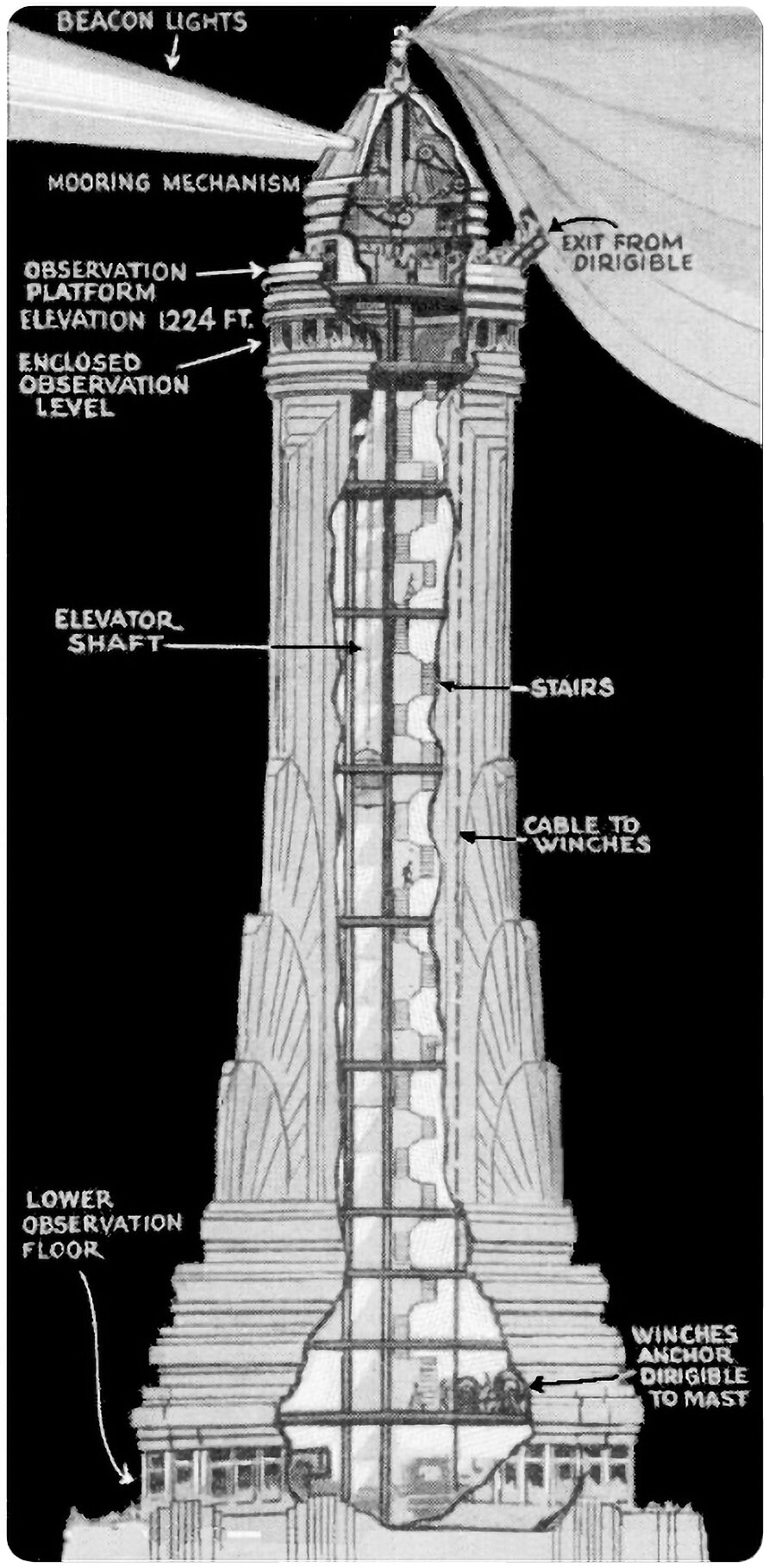
The Empire State Building’s Mooring Mast
Pictured above is an illustration from Popular Mechanics that shows the Empire State Building’s proposed mooring mast. This mast was designed to act as a dock for dirigibles, who could moor themselves to the top of the tower’s crown and load and unload passengers. It’s a wild idea, albeit completely impractical.
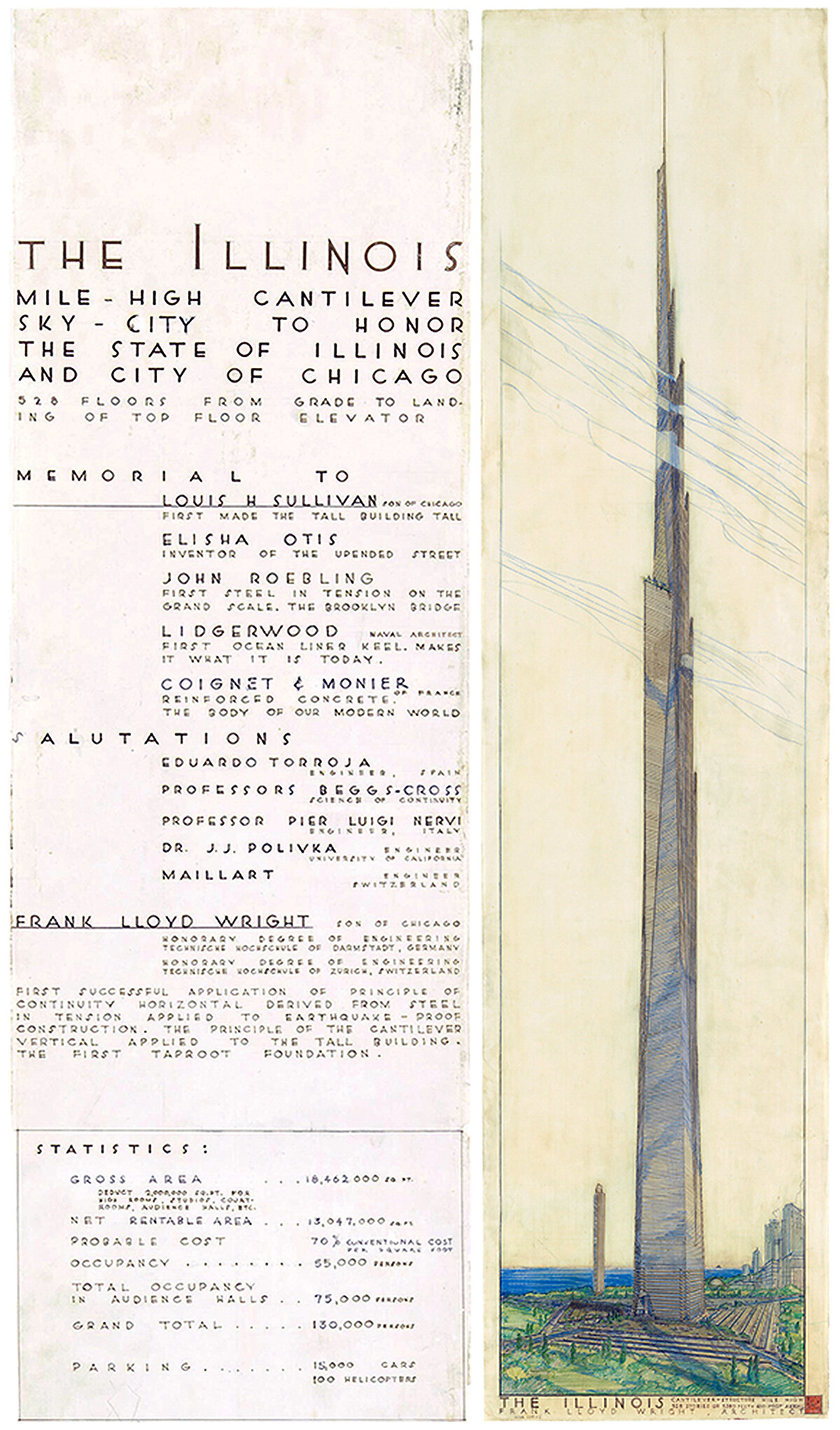
Frank Lloyd Wright’s Mile High Skyscraper Proposal
Frank Lloyd Wright was an outspoken advocate for low-density cities without skyscrapers. With this in mind, it’s hard to believe the tower design pictured above came from Wright. It’s called The Illinois, and it was planned to be a mile (1,609 meters, or 5,280 feet) in height. That’s more than four times the height of the Empire State Building, and nearly twice the height of the Burj Dubai.
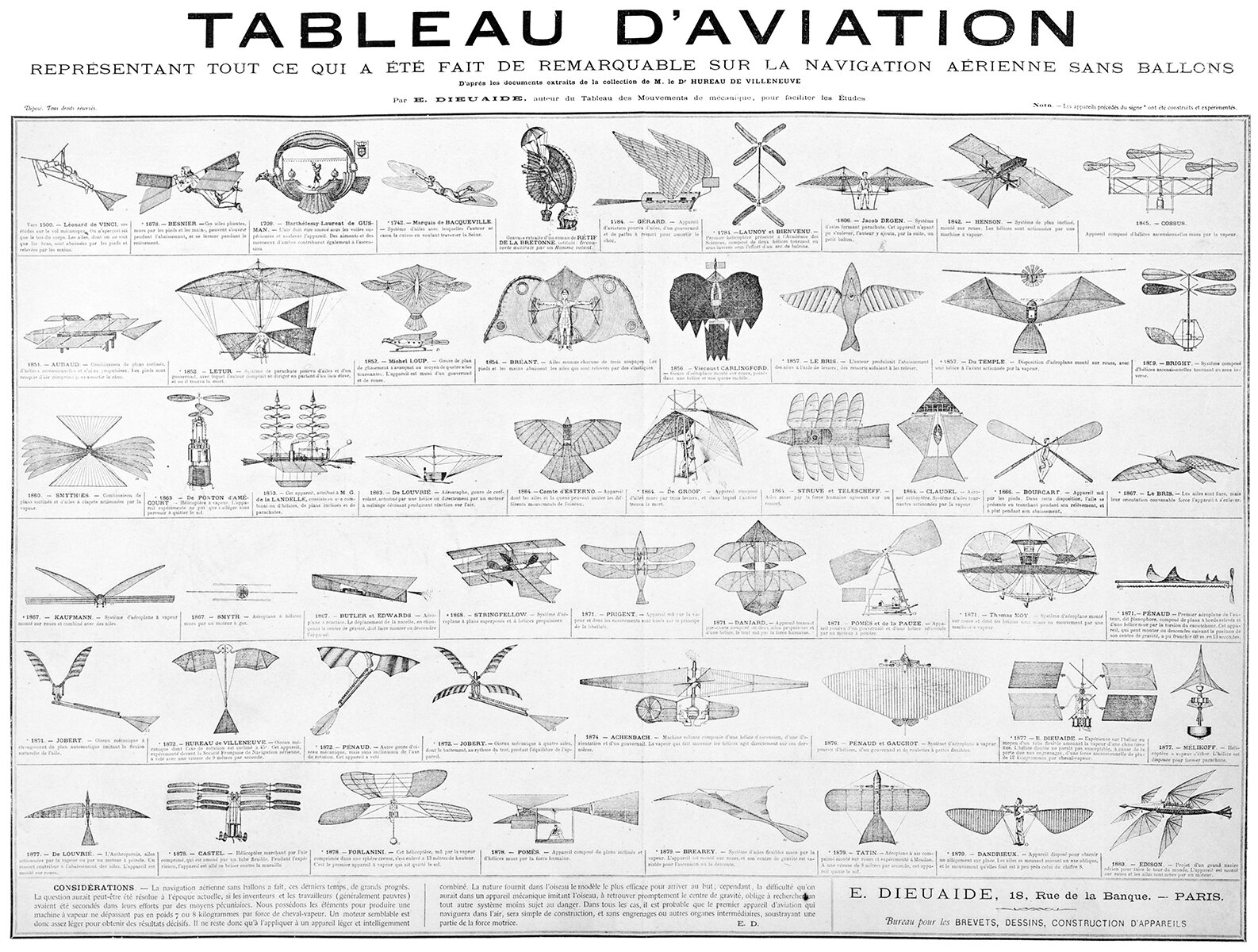
Tableau d’Aviation
The creativity and ingenuity on display throughout the history of flying machines is amazing. A quick survey of the table above shows the wide variety of ideas tried out before we humans successfully learned how to fly. One thing I love about this table is that it includes fictional flying machines as well as real prototypes. This shows that fictional designs can and have influenced the history of flight just as real prototypes have.
“The heavens call to you, and circle about you, displaying to you their eternal splendors, and your eye gazes only to earth.”
-From The Divine Comedy, by Dante Alighieri, Italian poet and philosopher, 1265-1321.
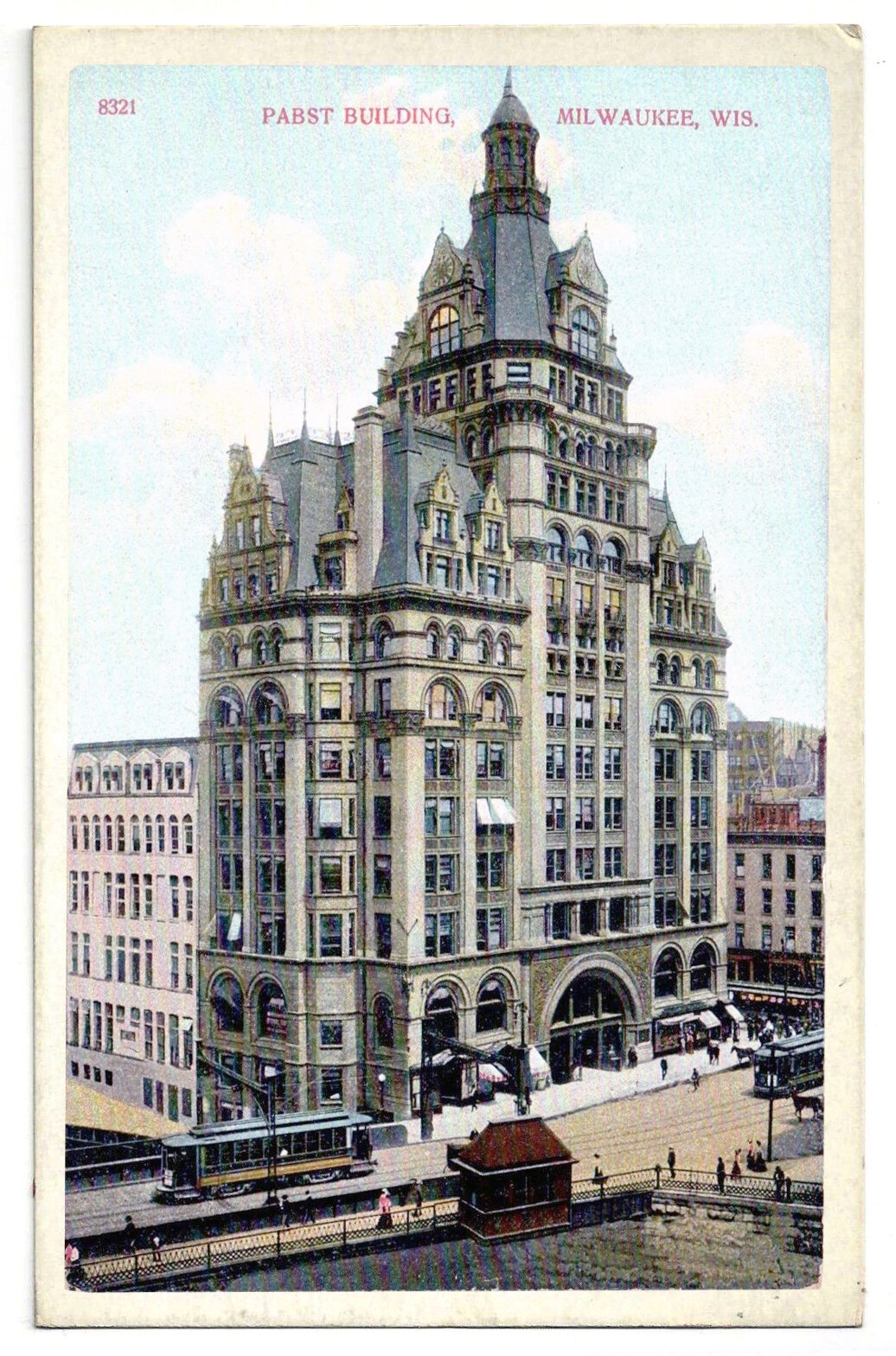

The Pabst Building and the Symbolism of Verticality
In 1890, Frederick Pabst purchased a plot of land at the center of downtown Milwaukee, on which he planned to build a headquarters for his brewing empire. A year later, the Pabst Building was complete. Standing fourteen stories and 235 feet (71 meters) tall, it was the tallest building in the city at the time, and it was a wonderfully detailed example of the Renaissance Revival style. Being Milwaukee’s tallest building was symbolic for Pabst and for the city, however his building’s dominance wouldn’t last as long as he’d hoped.

The Tale of the Ebony Horse
Pictured above is an illustration from The Tale of the Ebony Horse, which is a folk tale featured in the Arabian Nights. It tells the story of a mechanical horse that has the ability to fly. Throughout the tale, the horse bestows great power on those who know how to operate it, and it illustrates the power of verticality for the rest of us who cannot fly.
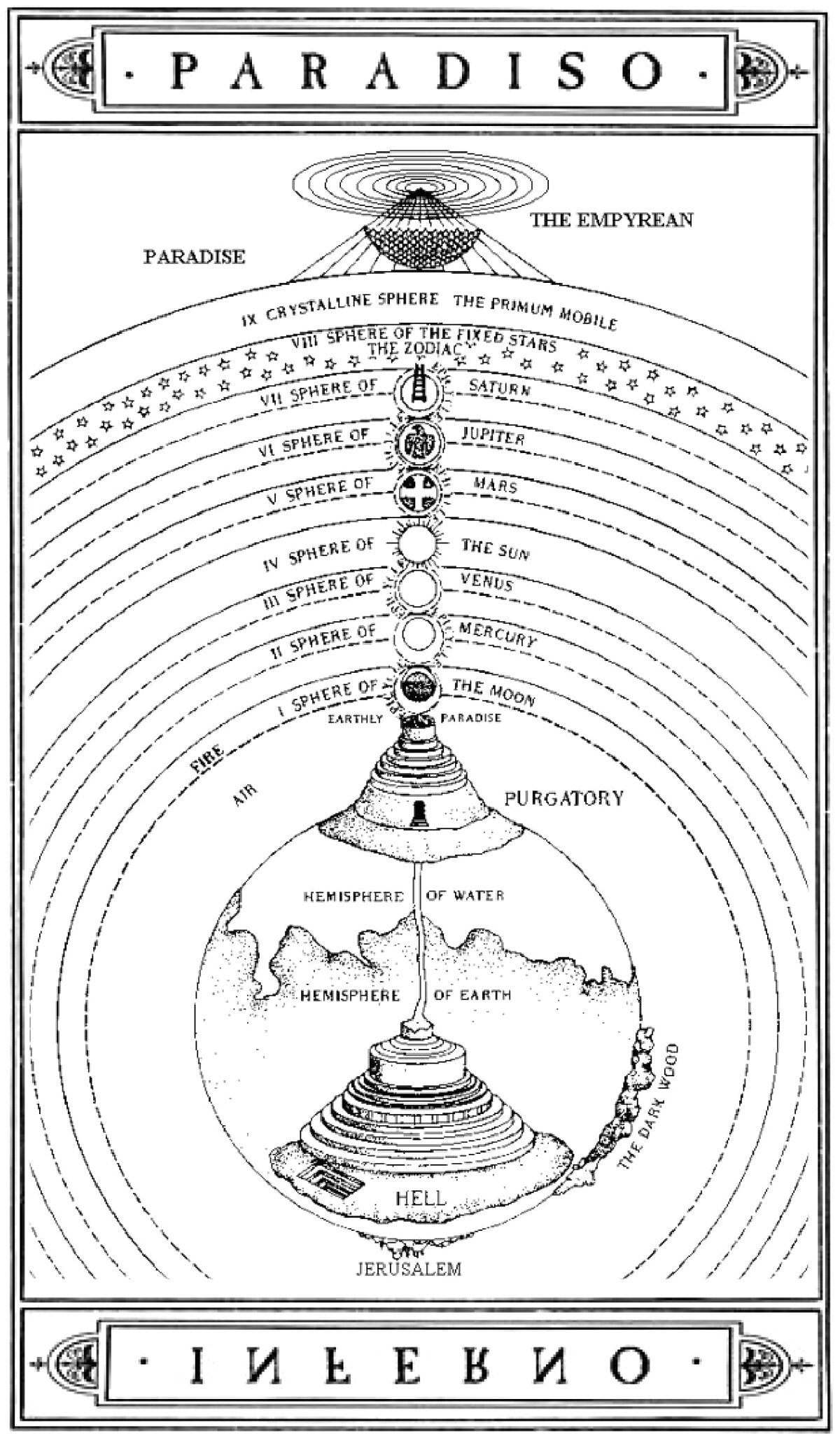
Dante’s Divine Comedy and the Vertical Worldview
Dante Alighieri’s epic poem La Divina Commedia, or The Divine Comedy in English, is widely considered one of the world’s greatest works of literature. It tells the fictional story of Dante and his soul’s experience after death. Throughout the story, Dante descends through Inferno, then ascends through Purgatorio and Paradiso. It’s a journey defined by the axis-mundi, and the entire work is rooted in verticality.
“He who occupies the high ground…will fight to advantage.”
-Sun Tzu, Chinese military strategist and philosopher, 544 BC-496 BC.

Alternate Realities : The Great Tower for London Competition
In 1890, an open competition was held to design the Great Tower for London in the soon-to-be-opened Wembley Park. The tower was to be the tallest in the world, and it would claim the title from the Eiffel Tower in Paris, completed the year before. An open competition was held, which received 68 submissions from all over the world. Together, these designs provide a rich cross-section of the world’s architectural taste at the time.
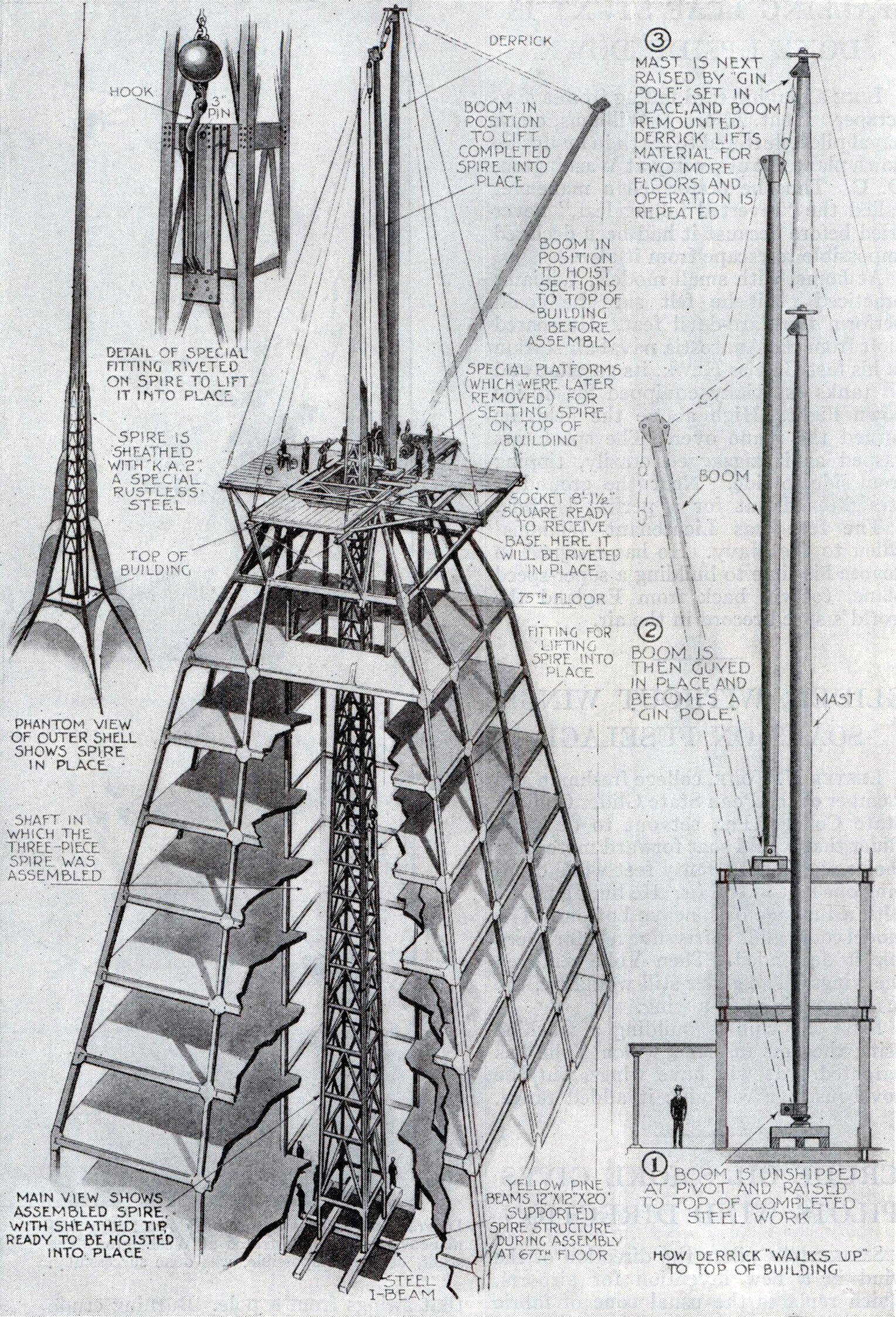
The Chrysler Building’s Hidden Spire
If you’re competing to build the tallest building in the world, and you want to conceal the final height until the last possible moment, how do you go about it? Well, you construct the spire inside the crown of the building, wait for your competitor to finish his tower, then lift your spire into place and take the title from him, of course.
